Glaciers—those magnificent rivers of ice—have been a hallmark of Earth’s climatic history, standing as sentinels of time. However, their majestic presence is rapidly vanishing. This article aims to unravel the intricate phenomenon of melting glaciers, delving into the reasons behind this drastic transformation, the implications of their decline, and what it means for our planet’s future.
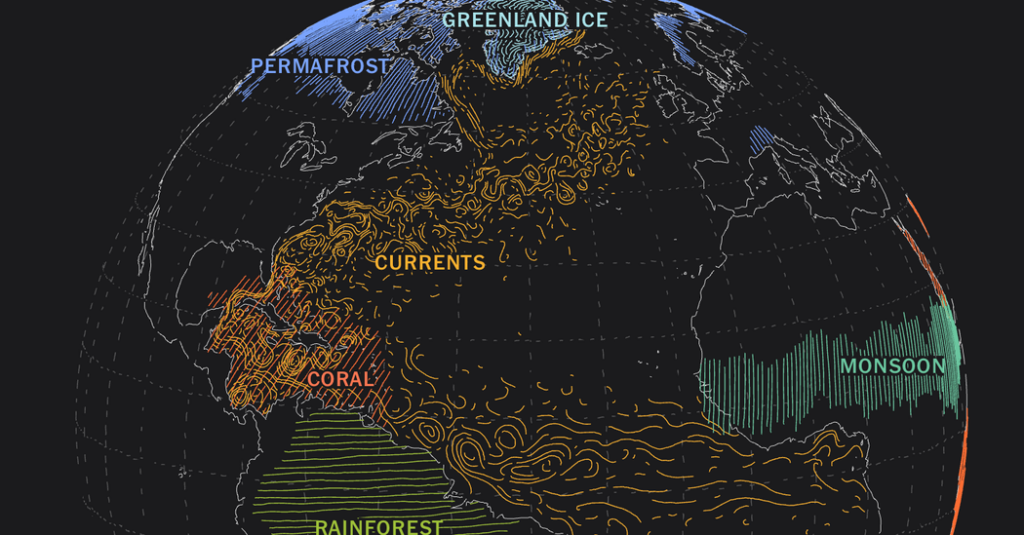
Glaciers cover about 10% of the Earth’s land surface. They are primarily found in polar regions but also exist in mountainous areas. As frozen reservoirs, they hold approximately 69% of the world’s freshwater. But, as we shall discover, these colossal ice formations are not static; they are dynamic entities responding to environmental changes.
To comprehend why glaciers are melting at an unprecedented rate, one must first understand the concept of climate change. Over the last century, human activity has released a substantial amount of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, causing the Earth’s average temperatures to rise. This phenomenon, known as the greenhouse effect, has severe consequences for glaciers.
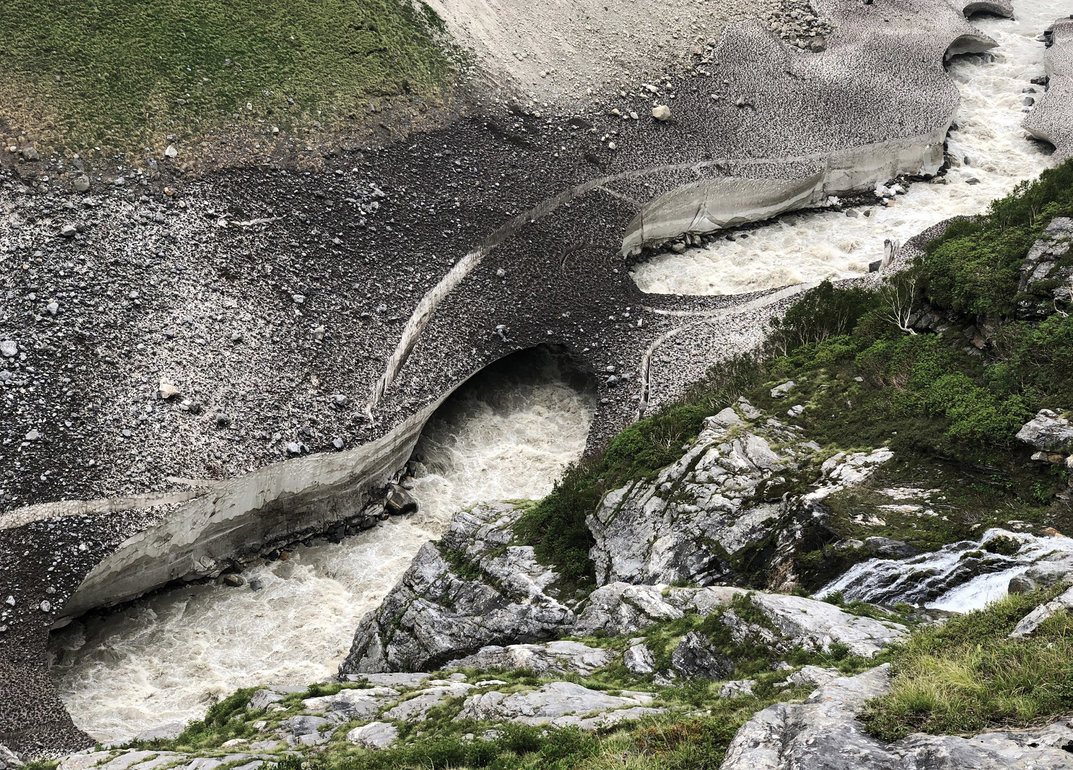
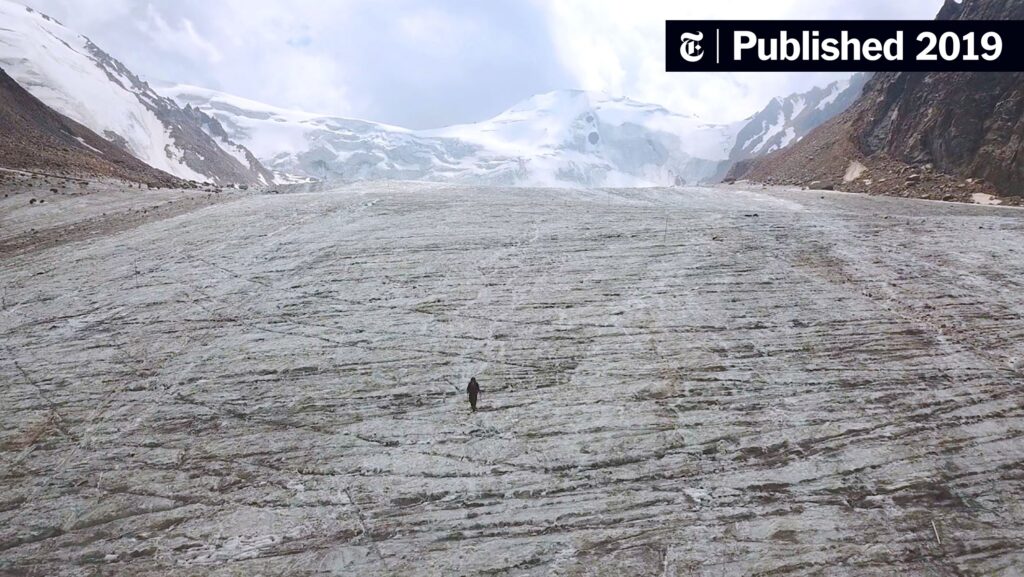
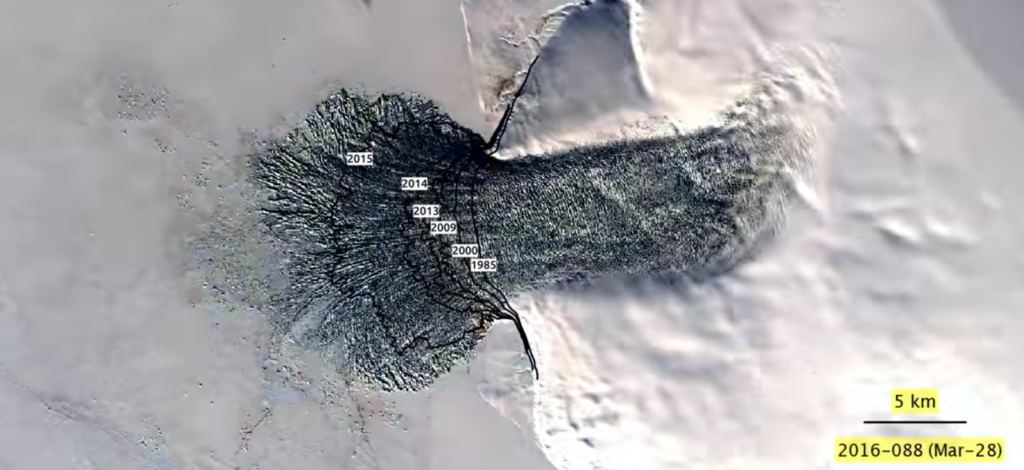
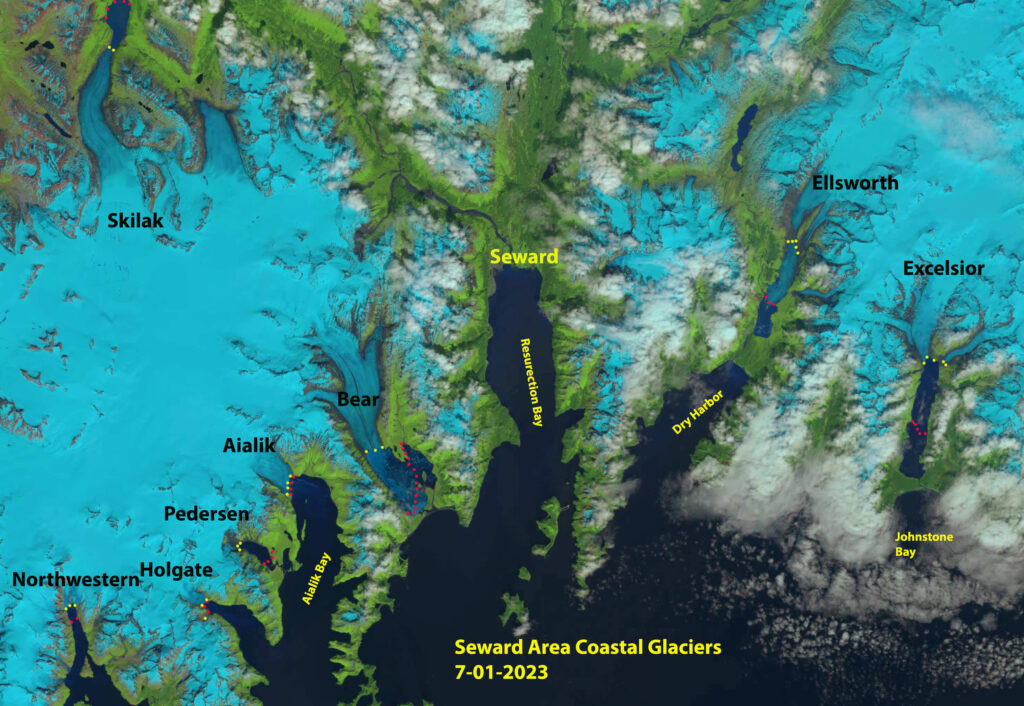
As global temperatures increase, the delicate balance of the Earth’s climate system is disrupted. Glaciers thrive in cold environments, where snowfall exceeds melting. With rising temperatures, however, this equilibrium is severely hampered. During the summer months, increased temperatures induce faster melting of glacier surfaces. Simultaneously, the winter snowfall that replenishes these icy giants is becoming less abundant. This creates a tough situation for the glaciers: they are losing mass, and faster than they can regain it.
In addition to temperature increases, another major factor contributing to glacier melt is wider climate variability. Extreme weather, resulting from climate change, leads to erratic precipitation patterns. Some regions may experience heavy snowfalls, while others suffer prolonged dry spells. This inconsistency adds another layer of stress on glaciers, further exacerbating their decline.
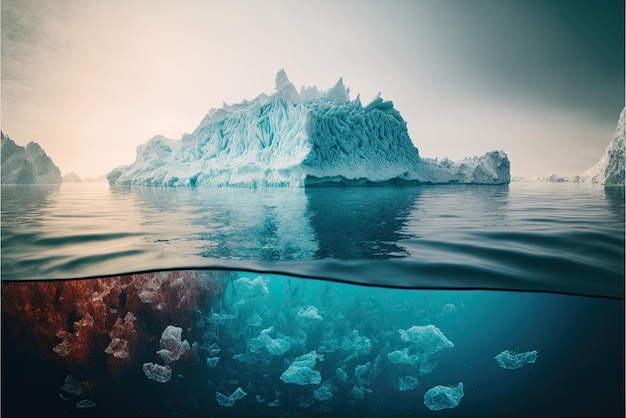
But why does the melting of glaciers matter? The repercussions of this phenomenon extend beyond picturesque landscapes and wildlife. One of the most pressing issues is the rising of sea levels. Glacial ice contributes to rising ocean levels as it melts, which can lead to flooding in coastal areas, threatening the livelihoods of millions. Moreover, cities like New York, Miami, and Tokyo are at risk of being partially submerged if this trend continues. Rising sea levels also compromise ecosystems, affecting marine life and biodiversity, and leading to the loss of habitat for many species.
Additionally, glaciers serve as essential freshwater sources for many regions around the world. In places like the Himalayas, glacial meltwater provides sustenance and drinking water to over a billion people. As glaciers recede, communities dependent on this critical resource could face dire water shortages. This scarcity can lead to agricultural decline, water conflicts, and increased migration, creating social and political instability.
Furthermore, the melt of glaciers contributes to geopolitical tensions. As these ice bodies shrink, access to previously unreachable natural resources, such as oil and gas, in the Arctic region becomes possible. This situation raises questions about ownership and the rights of indigenous peoples who have lived in harmony with these ecosystems for generations.
Now, consider the repercussions for wildlife. Many species, such as polar bears, depend on glaciers and ice-covered regions for their habitat. The rapid melting of ice strips these animals of their living spaces, pushing them into closer proximity with human settlements and creating conflicts. As if that were not enough, the altering of habitats can disrupt food chains, leading to drastic fluctuations in wildlife populations.
So, what can we do as responsible global citizens to mitigate this urgent crisis? Awareness is the first step. Understanding the importance of glaciers and the consequences of their melt fosters a sense of urgency and responsibility. Educational efforts should span a wide spectrum—from schools to communities—encouraging proactive discussions about climate change and its impacts.
Individual actions, while seemingly small, collectively wield significant power. Simple lifestyle changes can make a difference. Reducing energy consumption, lowering carbon footprints by utilizing public transport, recycling, and opting for renewable energy sources can contribute to combating climate change. Supporting policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions is another way to advocate for the Earth’s health.
Additionally, supporting organizations and initiatives focused on glacier research and conservation is essential. These groups work tirelessly to monitor glacial changes and advocate for policies that protect our climate system. They lead by example, demonstrating a commitment to sustainability that inspires others to partake in the cause.
In conclusion, the melting of glaciers represents a pivotal aspect of the broader narrative of climate change. It serves as a mirror reflecting the consequences of our actions on Earth. By comprehending the complexities surrounding glaciers and gleaning lessons from their decline, society can shift its path towards a more sustainable future. The time for inquiry, understanding, and proactive behavior is now. Only then can we ensure that future generations experience the majesty of glaciers, rather than merely reading about them in history books.







Leave a Comment