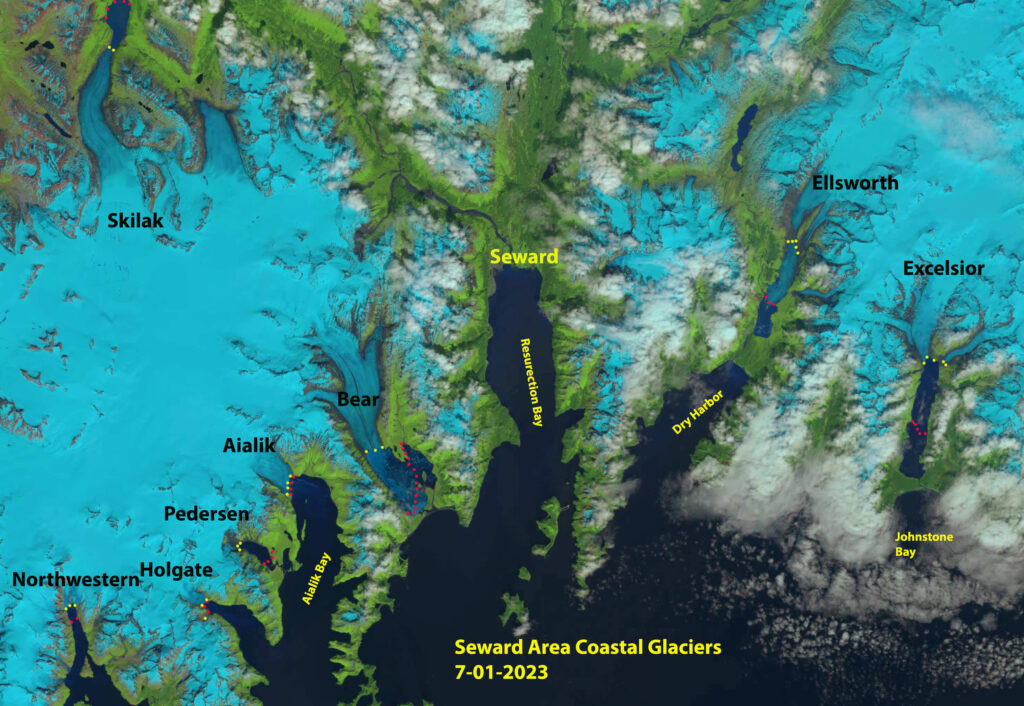
In recent years, the discourse surrounding climate change has taken on a more urgent tone, particularly regarding the phenomenon of glacier melting. As these magnificent ice giants, which have long stood as symbols of nature’s grandeur, succumb to rising temperatures, they bring about profound transformations that ripple through our ecosystems, economies, and societal frameworks. Have you ever pondered how the gradual disappearance of these colossal ice formations might be altering the very fabric of our planet? As we dissect this topic, we will explore five significant ways in which melting glaciers are reshaping our world.
1. Rising Sea Levels: The Imminent Tide
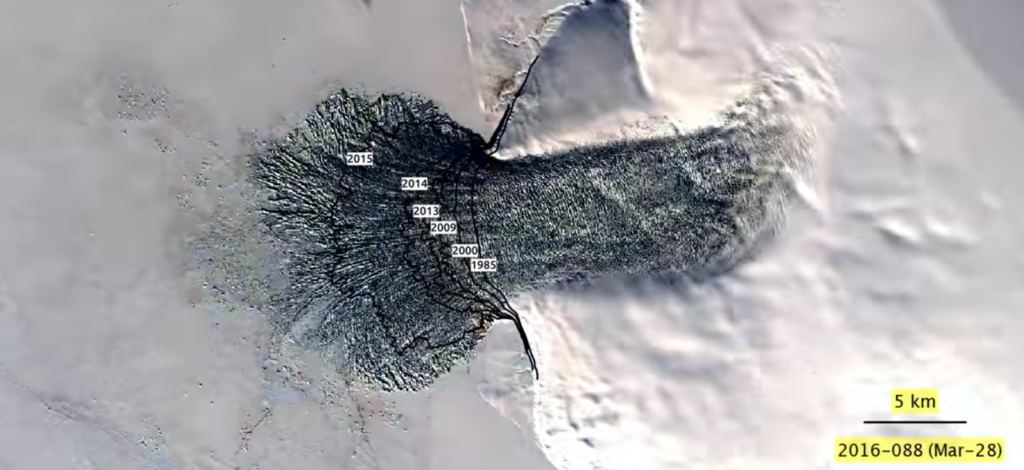
Perhaps the most pressing issue spawned from the melting of glaciers is the alarming rise in sea levels. Glaciers, having accumulated vast quantities of freshwater over millennia, are now releasing this precious resource into the oceans at an unprecedented rate. Predictions suggest a potential rise of several meters by the end of the century, drastically affecting low-lying coastal regions. Coastal cities like Miami, New Orleans, and Jakarta are already grappling with encroaching waters, which not only threaten infrastructure but also displace millions of inhabitants. One must ask: How will societies find resilience amid this existential threat when the land itself is receding?
2. Disruption of Ecosystems: A Ripple Effect
The ecosystems that flourish in glacial regions rely on the stability and predictability that glaciers provide. As these ice masses retreat, the intricate web of life that depends on them becomes increasingly vulnerable. Freshwater sources are altered, aquatic species face shifting habitats, and unique organisms that thrive in cold environments risk extinction. The shifts in ecosystems also impact surrounding wildlife, as food sources dwindle and migratory patterns become erratic. The cascading consequences of ecological disruption raise an unsettling question: How will biodiversity adapt to these rapid changes, and what might we lose in the process?
3. Altered Weather Patterns: The New Normal
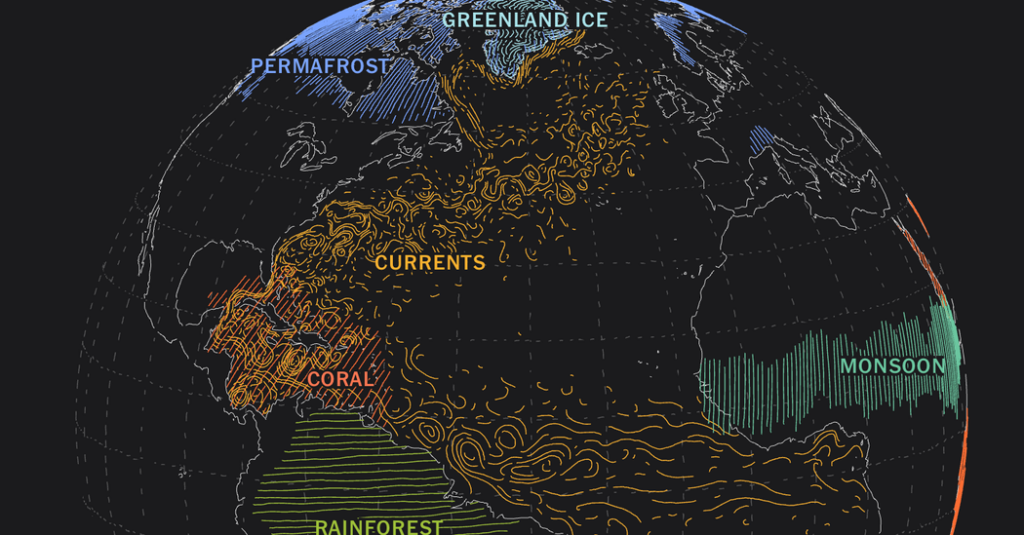
The melting of glaciers has a far-reaching influence on global weather patterns, contributing to irregular climate events. The influx of freshwater into the oceans can disrupt ocean currents, which play a pivotal role in regulating temperatures and weather systems worldwide. Regions may experience heightened storm intensity, prolonged droughts, or untimely precipitation, leading to a precarious balance for agricultural communities. As climate variability becomes the new norm, farmers and food producers face an array of challenges. One might wonder: Are we prepared to adapt our agricultural practices in response to increasingly erratic weather?
4. Thawing Permafrost: Unleashing Hidden Dangers
In tandem with glacier melting, the thawing of permafrost presents another alarming outcome. As temperatures rise, frozen ground—previously a robust barrier—begins to melt, releasing long-sequestered greenhouse gases such as methane and carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This phenomenon exacerbates global warming, creating a feedback loop that can accelerate the pace of climate change itself. The implications are dire, as scientists grapple with potential scenarios of further destabilizing our climate equilibrium. At this juncture, one must confront an unsettling dilemma: How do we, as stewards of the planet, curb the impending challenges posed by the release of these potent gases?
5. Economic Ramifications: The Price We Pay
The economic consequences of glacier melt are profound, affecting industries and livelihoods across the globe. Communities dependent on glaciers for tourism, water supply, and agriculture face critical challenges as their natural resources dwindle. The effects are not limited to local economies; they impact global markets as well. A decline in glacial runoff leaves regions grappling with water scarcity, directly influencing agricultural yields and food security. Additionally, rising sea levels increasingly necessitate costly adaptation measures, from building sea walls to relocating entire communities. One cannot help but question: Are we investing adequately in sustainable solutions, or are we waiting to be swept away by the tide of crisis?
As glaciers continue their retreat, the consequences are stark and multifaceted. The five avenues explored—rising sea levels, disrupted ecosystems, altered weather patterns, thawing permafrost, and enduring economic ramifications—underscore the extensive and often detrimental effects of this global phenomenon. It beckons humanity to engage in sustainable practices, innovative technologies, and collaborative efforts aimed at addressing these challenges. If we allow ourselves to remain entrenched in apathy, the question arises: How much longer can we ignore the siren call of our vanishing glaciers before they reshape our world beyond recognition?







Leave a Comment