Global climate change represents one of the most profound challenges facing humanity today. Its ramifications touch every facet of life on Earth, engendering a ripple effect that reverberates through ecosystems, economies, and societies. The intricate web of factors contributing to climate change is complemented by an array of potential solutions and adaptability strategies. This article seeks to elucidate the full range of global climate change, encapsulating its causes, consequences, and the multifarious approaches required to combat this existential threat.
Understanding Climate Change: The Fundamentals
At its core, climate change refers to long-term alterations in temperature, precipitation patterns, and other atmospheric conditions. Primarily driven by anthropogenic emissions—especially carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O)—the Earth’s climate system is undergoing unprecedented transformations. These changes stem largely from the combustion of fossil fuels, deforestation, and various industrial processes.
The greenhouse effect is a critical concept that illustrates how these gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to a gradual warming of the planet. While greenhouse gases exist naturally, human activities have significantly intensified their concentration, thereby exacerbating the rate of climate change.
Types of Climate Change
Climate change manifests in several distinct forms, each presenting unique challenges and implications. Some of the most pressing types include:
- Global Warming: The rise in Earth’s average surface temperature due to increased greenhouse gas concentrations is the most widely recognized aspect of climate change. This warming is linked to melting polar ice, rising sea levels, and altered weather patterns.
- Ocean Acidification: Absorption of excess CO2 by oceans leads to a decrease in pH levels, causing significant harm to marine ecosystems. Coral reefs, shellfish, and other marine life face dire consequences as their calcification processes are impaired.
- Extreme Weather Events: The frequency and intensity of hurricanes, droughts, heatwaves, and heavy rainfall are escalating, posing severe threats to human safety, agriculture, and infrastructure.
- Loss of Biodiversity: Ecosystems are collapsing as species struggle to adapt to rapidly changing climates. The extinction rates of wildlife are increasing alarmingly, disrupting ecological balances and diminishing the natural world’s richness.
The Consequences of Climate Change
The consequences of climate change extend far beyond rising temperatures. They ripple through natural systems, economies, and societal structures, engendering a host of crises.
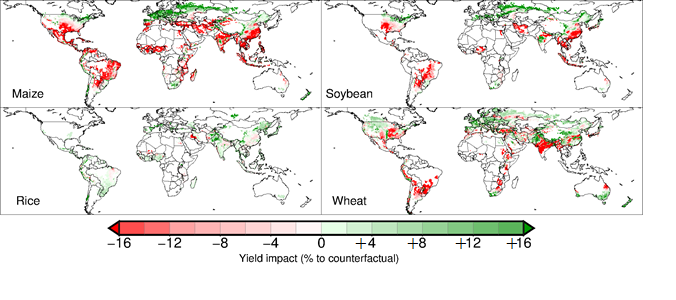
Rising sea levels, attributed to both thermal expansion and glacial melt, threaten coastal communities and ecosystems. Cities like Miami and New Orleans face dire futures as inundation risks rise. Moreover, as droughts become more prevalent in areas traditionally rich in agriculture, food security becomes jeopardized, leading to famine and economic instability.
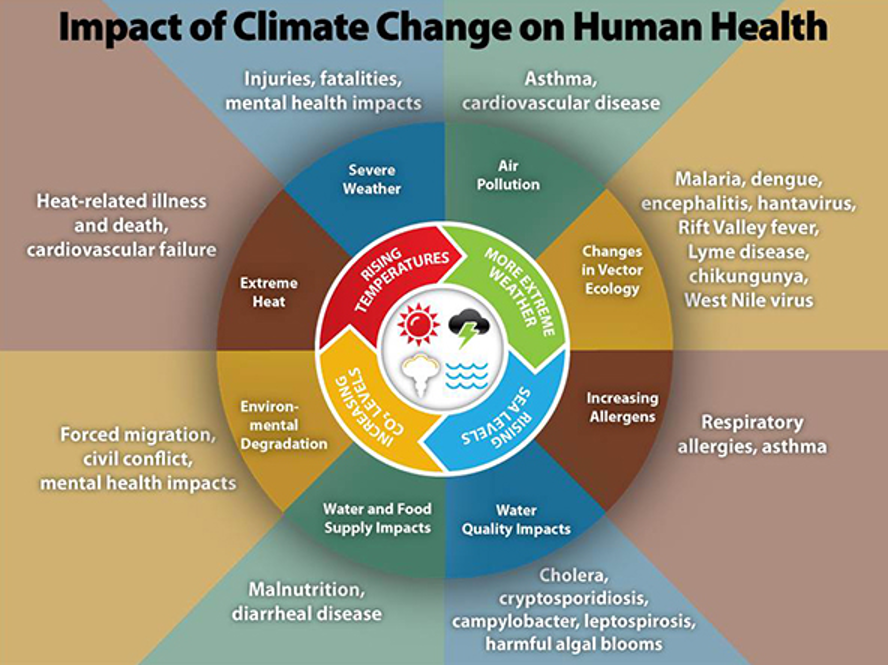
Moreover, health impacts are emerging as a significant concern. Heat-related illnesses, respiratory diseases exacerbated by poor air quality, and the spread of vector-borne diseases are rising. Vulnerable populations—particularly the elderly and low-income communities—are disproportionately affected, showcasing the social injustices that climate change perpetuates.
Mitigation Strategies: A Crucial Path Forward
Addressing climate change entails an urgent pivot towards mitigation strategies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, offer sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels. Transitioning to these energy forms not only curtails emissions but also fosters economic growth through job creation in emerging industries.
Moreover, energy efficiency improvements in transportation, buildings, and industrial processes can significantly reduce energy consumption. Innovations in technology, such as smart grids and electric vehicles, hold promise for a more sustainable future.
Reforestation and afforestation initiatives are vital, as trees serve as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Protecting existing forests and restoring degraded lands contribute to both climate mitigation and biodiversity conservation.
Adaptation: Preparing for an Uncertain Future
While mitigation is paramount, adaptation strategies are equally essential in preparing for the climate changes that are already set in motion. Communities must develop resilience against the impacts of climate change, transforming infrastructures to withstand extreme weather events. This includes enhancing stormwater management systems, constructing resilient buildings, and developing coastal defenses.
Agricultural adaptations, such as crop diversification and drought-resistant varieties, are crucial for maintaining food security. Moreover, early warning systems for natural disasters can save lives and mitigate financial losses, emphasizing the need for proactive planning.
International Cooperation: A Global Imperative
Climate change is a global issue that transcends national boundaries, necessitating international collaboration. Agreements like the Paris Accord underline the critical importance of collective action in shaping a sustainable future. Through shared commitments to reduce emissions, countries can forge a path toward stabilization of global temperatures.
Moreover, developed nations bear a responsibility to support developing countries in their climate endeavors, providing financial aid, technology transfer, and capacity-building measures. A just transition to a sustainable global economy requires inclusive frameworks that address historical inequalities.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The full range of global climate change elucidates the urgency of our collective action. With consequences far-reaching and often devastating, acknowledging the causes and embracing both mitigation and adaptation strategies is imperative. A united front is essential to combating this existential threat, ensuring a livable planet for generations to come. Each individual, community, government, and organization has a role to play in this monumental yet achievable endeavor.








Leave a Comment