Global warming is an omnipresent issue that transcends regions and borders, wielding a profound influence on our planet’s climate, ecosystems, and human society. To comprehend the intricacies of this phenomenon requires a thoughtful exploration of its underlying mechanisms, the evidence supporting it, and the multifaceted responses necessary to mitigate its impact. This guide aims to elucidate these complex concepts, presenting them in an accessible manner while ensuring the gravitas of the subject matter is retained.
Firstly, it is essential to define global warming within the broader context of climate change. Global warming specifically pertains to the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases—primarily carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide—trap heat, resulting in a greenhouse effect that exacerbates weather patterns worldwide. Understanding the distinction between global warming and climate change enables readers to appreciate the profound implications each has on ecological systems.
One of the key elements in grasping global warming is understanding its historical context. The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century, marked a significant turning point in human activity. The extensive burning of fossil fuels—coal, oil, and natural gas—triggered a surge in carbon emissions. This retrogression towards carbon-intensive energy sources has led to an unprecedented atmospheric concentration of CO2, now surpassing 400 parts per million. The historical emissions data corroborate the assertion that human interventions are at the heart of this warming crisis.
Furthermore, scientific evidence supporting the reality of global warming spans various disciplines, from glaciology to oceanography. One stark indicator of climatic shifts is the retreat of polar ice caps and glaciers, leading to rising sea levels. Projections estimate that, if unchecked, global sea levels could rise between one and four feet by the end of the century, imperiling coastal cities and ecosystems alike. Likewise, ocean temperatures have risen concomitantly, resulting in coral bleaching events and altered marine biodiversity.
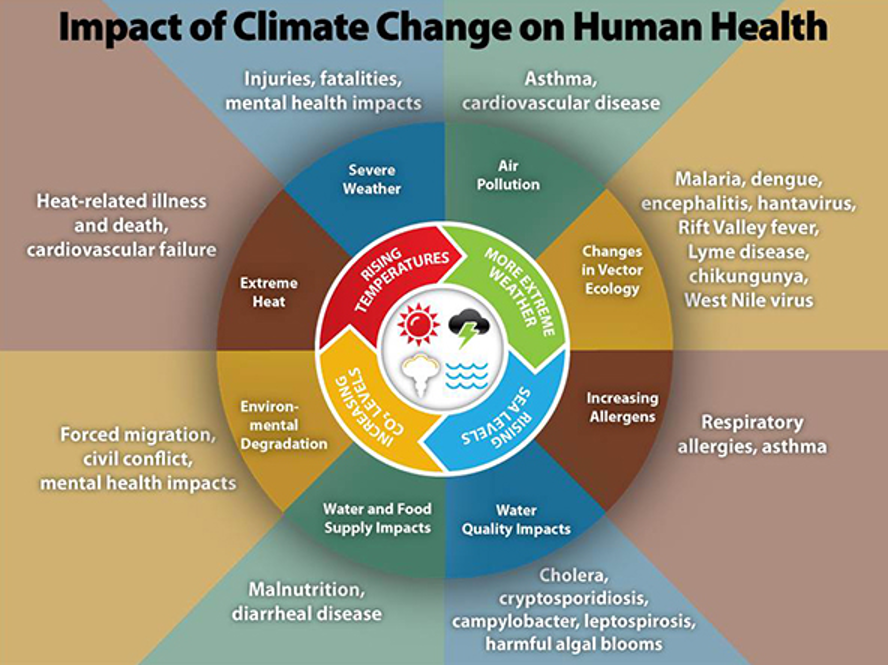
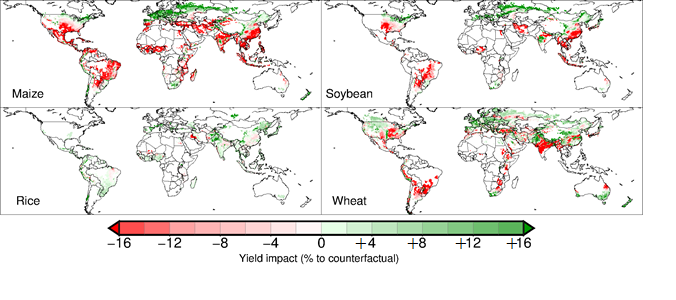
The implications of these changes extend beyond mere temperature increases. The phenomenon of global warming engenders a cascade of events, including altered weather patterns manifesting as extreme weather phenomena. Storms have grown more intense, droughts more severe, and wildfires increasingly common. Such fluctuations strain agricultural systems, threaten food security, and challenge infrastructural stability, particularly in vulnerable regions already grappling with socio-economic challenges.
In addressing this vast challenge, it is crucial to explore the myriad of solutions that exist, categorized broadly into mitigation and adaptation strategies. Mitigation seeks to reduce or stabilize the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, primarily through the transition to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower. For instance, innovations in energy efficiency, carbon capture technologies, and reforestation efforts serve as pivotal strategies in the fight against increasing temperatures.
Adaptation, on the other hand, refers to the adjustments made in response to the current impacts of global warming. This can include constructing resilient infrastructure, developing drought-resistant crops, and implementing water management systems suitable for changing climates. A holistic approach that integrates both mitigation and adaptation is vital, particularly in regions where climate change poses immediate threats to livelihoods and ecosystems.
Engagement from various sectors—including government bodies, corporations, and communities—plays a fundamental role in orchestrating effective responses. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, exemplify the collective commitment to limiting global temperature rise to below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. The success of these initiatives hinges on sustained cooperation and accountability between nations and organizations, emphasizing that the ramifications of inaction have no geographic limits.
A pivotal aspect of the discourse around global warming is education and awareness. Disseminating knowledge empowers individuals to advocate for sustainable practices and make informed choices about their consumption patterns. Initiatives that promote environmental literacy can galvanize grassroots movements and foster a culture of stewardship, underscoring the critical role of informed citizenry in combatting climate change.
It is imperative to recognize that while global warming poses alarming challenges, it also presents opportunities for innovation and collaboration. The increasing urgency surrounding climate issues has produced an incubator for technological advancements, sustainable business models, and policy innovation. Businesses that adopt environmentally friendly practices not only contribute to mitigating climate impacts but can also reap economic benefits by tapping into burgeoning green markets.
In summation, understanding global warming is a multifaceted endeavor that bridges history, science, policy, and personal responsibility. The necessity for comprehensive analysis and concerted action is central to effectively addressing this existential threat. By acknowledging the gravity of global warming, championing informed dialogue, and committing to proactive solutions, humanity stands a better chance of securing a sustainable future for generations to come. Engaging with this knowledge not only equips individuals with the tools to respond but embodies a crucial step toward a collective movement aimed at restoring harmony with our planet.







Leave a Comment