The phenomenon of global warming represents a paramount challenge to our contemporary existence and the health of our planet. In its most succinct articulation, global warming refers to the long-term elevation of Earth’s average surface temperature, a change chiefly driven by an augmentation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere due to anthropogenic activities. As climate scientists endeavor to unravel this complex tapestry of environmental shifts, it is vital to comprehend the multifaceted causes, concerning effects, and the overarching implications of such profound transformations.
Causes of Global Warming
At the crux of global warming lies the enhanced greenhouse effect, an intricate process wherein certain gases trap heat within the Earth’s atmosphere. These gases, predominantly carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, accumulate as a result of various human activities. For instance, the combustion of fossil fuels—predominantly for energy needs—emits an alarming quantity of carbon dioxide. Vehicles, industries, and power generation facilities are veritable culprits, releasing vast amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. Furthermore, deforestation exacerbates this situation; trees, essential for sequestering carbon, are felled to make way for agriculture, urban development, and logging.
Another significant contributor is methane, a gas with a far greater potential to trap heat than carbon dioxide, albeit in smaller quantities. Methane emissions arise from agricultural practices, especially livestock digestion and manure management, alongside natural gas production. Similarly, nitrous oxide, stemming from agricultural runoff and the use of synthetic fertilizers, emerges as a formidable adversary in the battle against global warming.
In addition to these more recognized causes, the impact of industrial processes cannot be overlooked. The production of concrete, steel, and plastics involves chemical reactions that release additional greenhouse gases, contributing further to the atmospheric crisis. Thus, the grasp of global warming expands to encompass a plethora of human machinations that disrupt the delicate balance of our climatic systems.
Effects of Global Warming
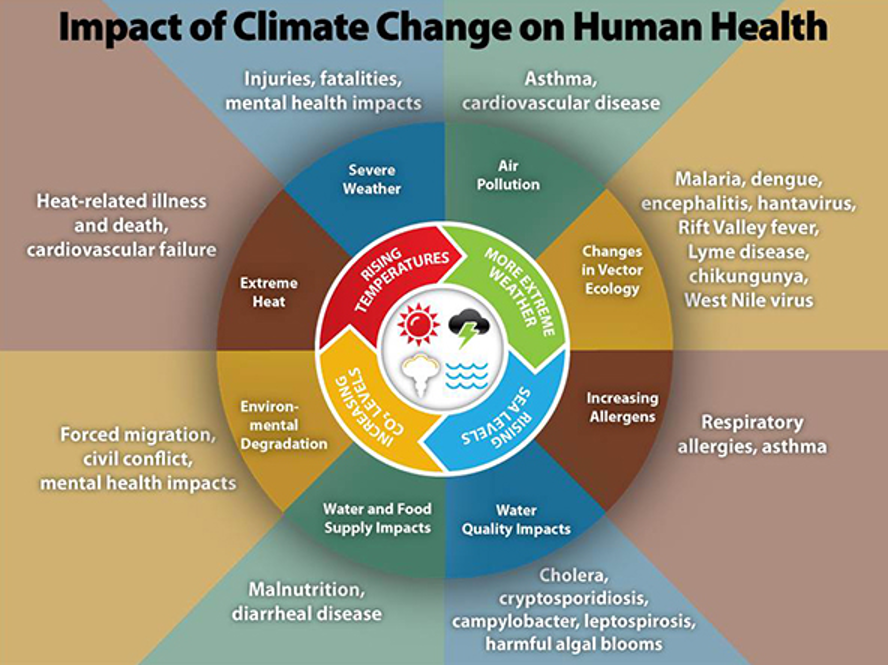
The repercussions of global warming are as varied as they are profound. One of the most conspicuous effects is the rise in global temperatures, which leads to a cascade of environmental changes. The melting of polar ice caps and glaciers results in elevated sea levels, putting coastal communities at risk. An estimated 640 million people live in areas prone to flooding, and without urgent intervention, entire nations could disappear beneath the waves.
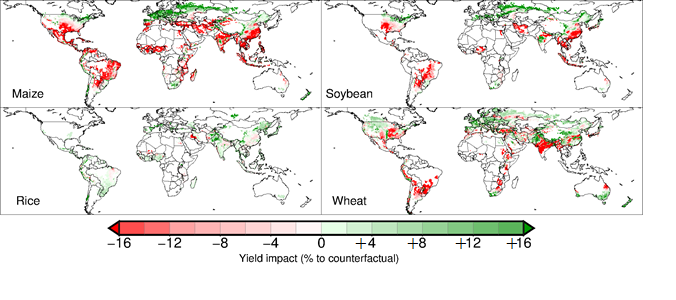
Moreover, changes in temperature and precipitation patterns engender extreme weather events that have become alarmingly frequent. Hurricanes, wildfires, droughts, and heatwaves have escalated in intensity and duration, wreaking havoc and endangering lives. Agricultural practices are disproportionately affected, as shifting climate zones disrupt traditional farming cycles. Crop yields could plummet, leading to food insecurity in regions already grappling with poverty.
Beyond immediate ecological concerns, the effects of global warming extend to biodiversity. Species unable to adapt to rapidly changing habitats face extinction, leading to a catastrophic loss of biodiversity. Coral reefs, which support vibrant ecosystems, are particularly vulnerable, with rising ocean temperatures and acidification resulting in coral bleaching and subsequent mortality.
Furthermore, public health is undergoing a grim transformation as the effects of global warming intertwine with societal structures. Higher temperatures facilitate the spread of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever, as previously inhospitable areas become suitable for disease-carrying organisms. Air quality suffers, aggravating respiratory diseases and fueling health crises, particularly among vulnerable populations.
Meaning and Implications
Understanding global warming transcends mere recognition of its causes and effects. It necessitates a contemplation of our collective relationship with the environment. The essence of global warming is a clarion call to re-evaluate our habits and practices. It forces society to confront uncomfortable truths about consumption, economic growth predicated on fossil fuels, and the existential risks posed by rising temperatures.
This understanding necessitates action on multiple fronts; it beckons innovations in renewable energy, the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices, and a shift towards circular economies. It urges individuals to pivot from disposable consumerism to sustainable choices. Each action, no matter how minuscule it may seem, forms a part of a grander mosaic of resistance against the tide of global warming.
Furthermore, engaging in dialogue about global warming compels a reassessment of our values. It is imperative to cultivate empathy for future generations who will inherit the consequences of today’s decisions. Through this lens, global warming is not merely a scientific challenge but a profound ethical dilemma, urging a collaborative international response and unwavering commitment to preserving our planet’s health.
Conclusion
Global warming encapsulates a multifarious challenge forged from human activity, its effects reverberating across the globe. From rising temperatures and unpredictable weather patterns to profound implications for biodiversity and public health, it is evident that the time for action is now. As we navigate the tumultuous waters of environmental change, we must coalesce our knowledge and compassion into a formidable force for change, fostering a future where harmony between humanity and nature can endure.







Leave a Comment