As we observe the majestic beauty of glaciers towering over remote landscapes, a playful question emerges: What would happen if these ancient ice behemoths disappeared overnight? It is a fantastical thought, yet it unveils a dark tapestry woven with intricate and alarming consequences. The implications of glacial melting extend far beyond serene vistas; they evoke a series of ecological and socio-economic challenges that warrant our urgent attention.
The phenomenon of glacial melting is inherently tied to climate change, primarily fueled by anthropogenic activities. As global temperatures continue to rise, glaciers—nature’s frozen reservoirs—begin to succumb to the relentless heat. The consequences ripple across several dimensions, affecting not only the environment but also human societies and economies. To understand the gravity of this crisis, we must delve into the myriad repercussions that glacial melting brings.
Rising Sea Levels
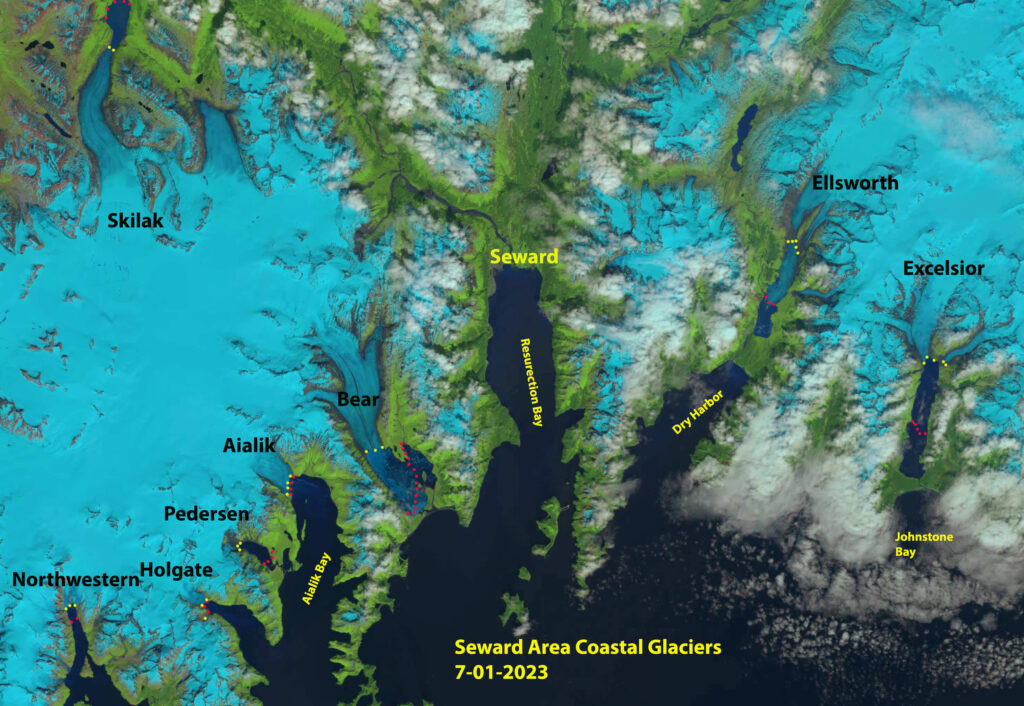
The first and perhaps most palpable consequence of glacial melting is the inexorable rise in sea levels. Glaciers and polar ice sheets constitute a significant portion of the Earth’s freshwater reserves. As they melt, colossal volumes of water flow into our oceans. According to estimates, completely melting the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets could result in a sea-level rise of more than 60 meters. This scenario, albeit extreme, is a stark reminder of the potential for catastrophic flooding. Coastal municipalities and island nations are particularly vulnerable, grappling with the risk of displacement, loss of habitat, and erosion of infrastructure.
Altered Ecosystems
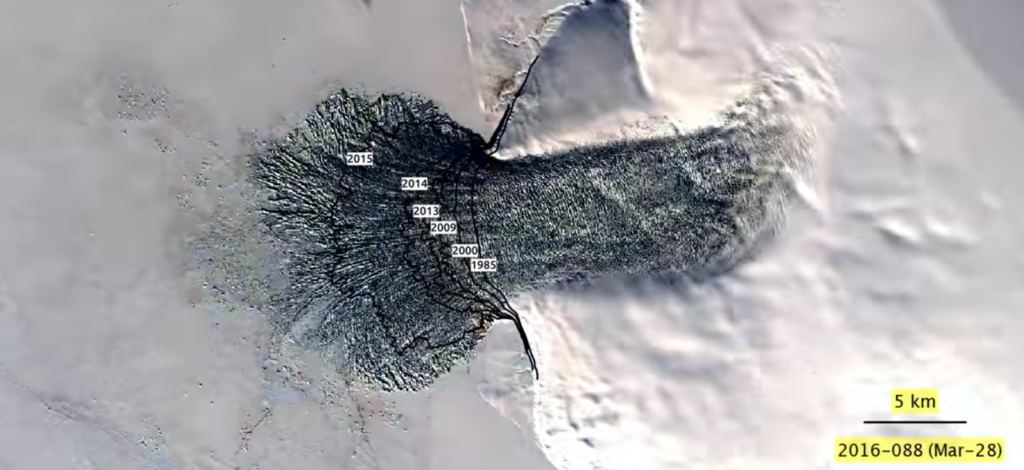
In addition to rising sea levels, glacial melting disrupts delicate ecosystems. Glaciers serve as critical sources of freshwater for a multitude of species and human populations. As the glaciers recede, the freshwaters that many fish and other aquatic organisms depend on become more saline, leading to biodiversity loss. Aquatic ecosystems are further challenged by increased sedimentation, as melting glaciers expose soil and rock that are washed into rivers. Species that thrive in specific temperature ranges may find their habitats decimated, uprooting the entire food chain.
Impacts on Water Supply
The implications for freshwater supply are equally concerning. Millions of people across the globe, particularly in mountainous regions, rely on glacier-fed rivers. As glaciers continue to recede, short-term benefits may emerge in the form of increased river flow. However, as glaciers diminish in size, the sustenance they provide will dwindle, leading to an eventual water scarcity crisis. This precarious balance poses existential threats to agricultural practices, urban water management, and ultimately, human survival.
Climate Feedback Loops
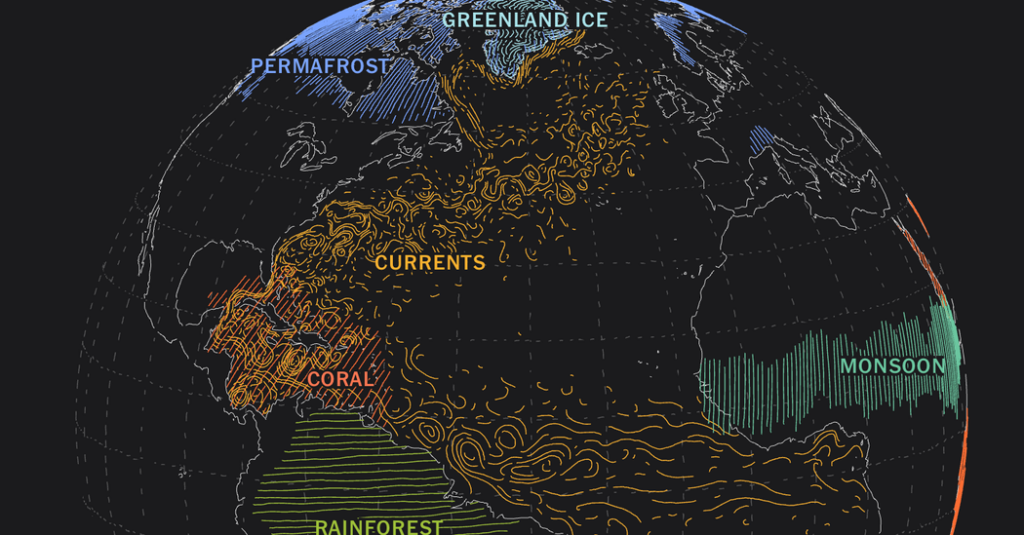
Glacial melting does not merely influence our physical landscapes; it also exacerbates climate change through intricate feedback loops. Glaciers and ice sheets reflect sunlight, contributing to the Earth’s albedo, or reflective surface. As these icy bastions disappear, darker ocean waters and land surfaces absorb more sunlight, further escalating warming trends. This reciprocal relationship intensifies the urgency of the climate crisis, thereby creating a vicious cycle that perpetuates glacial melting.
Permafrost Thawing
Another alarming consequence of glacial melting is the thawing of permafrost, a phenomenon often overlooked in discussions about climate change. Permafrost, which stores vast amounts of carbon in the form of frozen organic material, becomes unstable as temperatures rise. When thawed, this material decomposes, releasing significant quantities of carbon dioxide and methane—a potent greenhouse gas—with implications for climate change that are difficult to quantify. The act of glacial melting sets off a chain reaction that could accelerate global warming to unprecedented levels.
Cultural and Economic Impacts
Beyond environmental repercussions, glacial melting poses significant challenges to economies and cultures. Indigenous communities that have relied on glaciers for sustenance, transportation, and spiritual connection are placed in jeopardy. The depletion of their local resources could erode traditional ways of life, leading to cultural disintegration. Economically, agriculture reliant on glacial meltwater could suffer as water shortages emerge, potentially destabilizing food systems and exacerbating poverty in already vulnerable regions.
International Tensions
As glaciers melt and freshwater resources dwindle, the potential for conflict over water resources intensifies. Rivers originating in glacial regions often traverse multiple countries, making them focal points for geopolitical tension. Nations may find themselves competing for dwindling supplies, leading to diplomatic strains that could escalate into conflict. The Tower of Babel that is global geopolitics becomes yet more convoluted when the delineation of resources intersects with national interests.
A Call to Action
These consequences of glacial melting present not only formidable challenges but also a clarion call for action. Addressing climate change—our shared nemesis—is imperative. Transitioning toward sustainable energy alternatives, enhancing water conservation efforts, and advocating for comprehensive climate policies are crucial steps in mitigating these troubling outcomes. It’s essential to foster global cooperation to develop adaptive strategies that will protect both human and ecological communities in the face of inevitable change.
In conclusion, the breathtaking beauty of glaciers should serve as a solemn reminder of the perils they face. As they diminish, they unveil a tapestry of consequences that impact ecosystems, economies, and cultures. It is incumbent upon us to confront these challenges head-on, ensuring that we preserve not just the ice but the intricate web of life that relies upon it. The time for decisive action is now, and the survival of our planet may depend on it.







Leave a Comment