In the complex dance of our planet’s climatic system, the greenhouse effect acts both as a guardian and a potential adversary. Imagine this: what if the very atmosphere that nurtures life as we know it begins to spin out of control? This introspective question prompts us to unravel the layers of the greenhouse effect, exposing the delicate balance of energy that sustains Earth’s ecosystems.
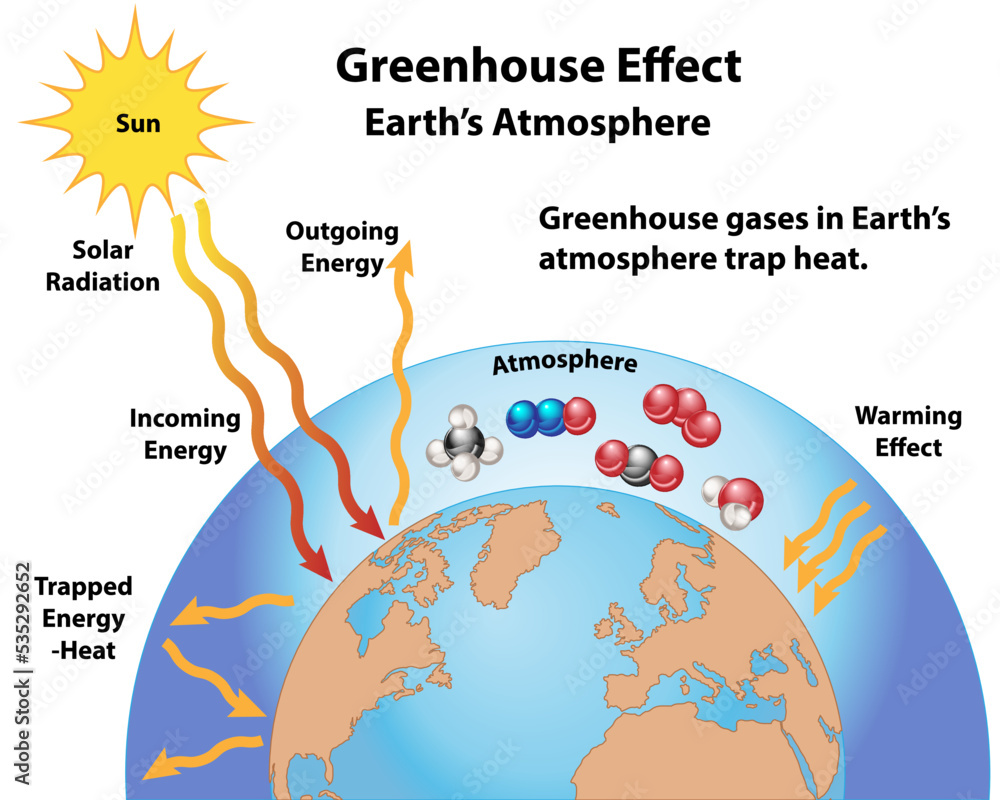
To embark on this journey, we first need to grasp the foundational science underpinning the greenhouse effect. At its core, this phenomenon involves the absorption and re-emission of infrared radiation by gases in the atmosphere. Without these greenhouse gases, our planet would languish in a frigid state, inhospitable to the myriad life forms that thrive today.
Under normal circumstances, the Earth absorbs sunlight, converting light energy into heat. This process warms the surface, which in turn emits energy in the form of infrared radiation—essentially heat. However, not all of this radiation escapes into the void of space. Enter greenhouse gases: carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor. These gases, akin to a cozy blanket, trap some of this heat, preventing it from dissipating. This retention of warmth is crucial; it maintains a stable climate conducive to life.
However, this vital equilibrium is increasingly jeopardized by human activity. The exponential increase in fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes has led to a surge in the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Current atmospheric CO2 levels are unprecedented in the last 800,000 years, according to geological records. This spike in greenhouse gases results in an enhanced greenhouse effect, a phenomenon that intensifies global warming and brings dire consequences.
So, how exactly do these gases contribute to climate change? Consider infrared radiation—a form of energy that is invisible to the naked eye, yet powerful enough to alter the delicate climate balance. When greenhouse gases absorb this energy, they become excited. This excitement translates into movement: these molecules vibrate and release energy in all directions, including back toward the Earth’s surface. This process is akin to a re-emission cycle, where the planet becomes a passive recipient, absorbing heat rather than allowing it to escape.
This is where the challenge lies: as we increase our greenhouse gas emissions, we unwittingly intensify this cycle, raising global temperatures higher and higher. The consequences are staggering. Polar ice caps are melting, ecosystems are shifting, and we face an increase in extreme weather events—from devastating floods to scorching heatwaves. Each anomaly is a stark reminder of how intertwined our actions are with the health of our planet.
To understand these effects better, we can categorize the impacts into several crucial domains. First, consider biodiversity. As climate patterns shift, many species face extinction as their natural habitats become inhospitable. Coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea,” are particularly vulnerable, with coral bleaching events on the rise, driven by increasing ocean temperatures and acidity.
Next, let’s delve into the realm of human health. Rising temperatures contribute to the proliferation of vector-borne diseases. As warmer climates expand, so do the territories of mosquitoes and ticks, introducing illnesses like malaria, dengue fever, and Lyme disease to new populations. The fight against climate change thus becomes intrinsically linked to the fight for human health.
Moreover, consider the socio-economic implications. Agriculture, a cornerstone of human sustainability, experiences volatility due to changing weather patterns. Droughts and unpredictable rainfall challenge food security worldwide. With millions already suffering from hunger, the onslaught of climate change threatens to exacerbate these crises, calling for immediate and sustained action.
As the realities of the enhanced greenhouse effect unfold, one must ask: what can we do? The answer lies in foundational changes to our systems. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, embracing energy efficiency, and advocating for sustainable agricultural practices can help mitigate our impact. Moreover, reforestation efforts can serve as both a carbon sink and a method to restore biodiversity.
In summation, the complexity of the greenhouse effect epitomizes the intricate interplay between natural processes and anthropogenic influences. A nuanced comprehension of this phenomenon underscores the urgency for collective action. The existential challenge posed by the greenhouse effect beckons each of us to reflect on our contributions to this planetary crisis and adopt sustainable practices in our daily lives. Will we rise to the occasion and become stewards of our environment, or will we allow this crucial equilibrium to unravel? The choice is ours to make.








Leave a Comment