The greenhouse effect—terms that may evoke vague notions of climate change, elevated temperatures, or acrid air—is a phenomenon intricately woven into the intricate tapestry of our planet’s climate system. It encapsulates a natural process that retains warmth in the Earth’s atmosphere, akin to how glass holds heat in a greenhouse. However, the simplicity of this concept can often obscure the profundity of its implications. As we delve deeper, we illuminate its significance and unravel the threads connecting this scientific principle to the broader narrative of environmental stewardship.
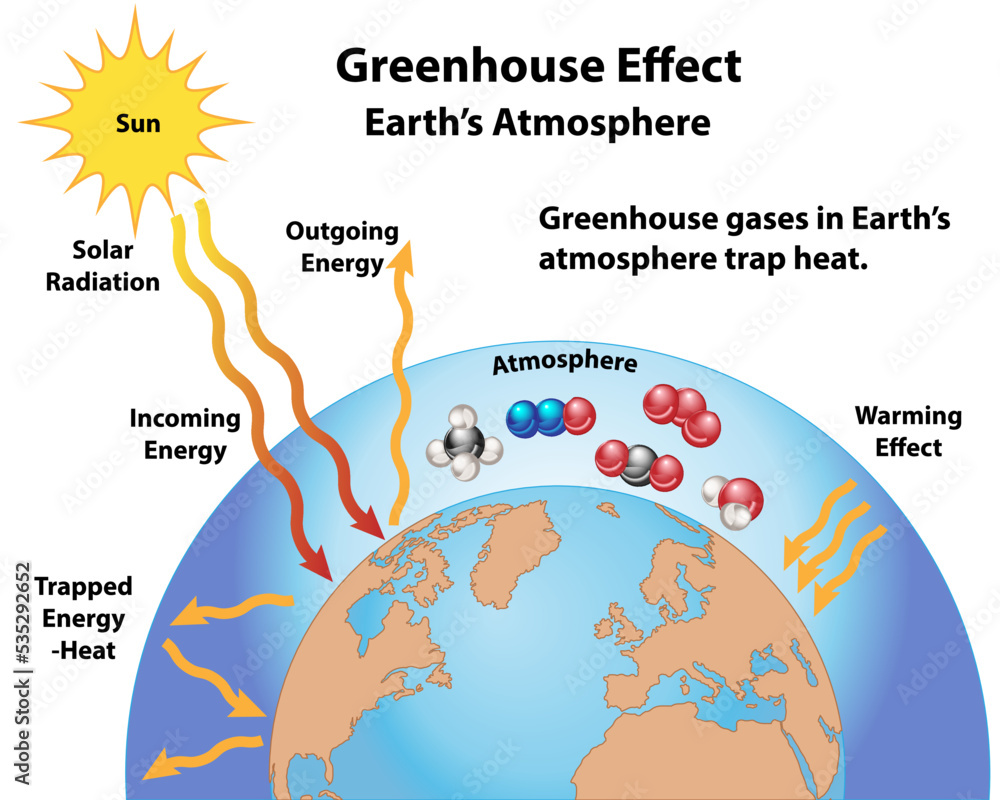
To elucidate the greenhouse effect, let us commence with the fundamentals. The Earth receives energy from the sun in the form of solar radiation. A portion of this energy is absorbed by the Earth’s surface, while some is reflected back into space. This interaction is crucial. It maintains a balance that sustains life. Without it, we would exist in perpetual frost, inhospitable to the array of biodiversity we cherish. However, this dynamic equilibrium is delicate, and human activity has disrupted it, tipping the balance towards an unnatural state.
The atmosphere plays a pivotal role in this process. Within it resides a collection of gases known as greenhouse gases (GHGs). These include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), among others. Their function is vital: they trap heat that would otherwise escape. Picture them as a warm blanket enveloping the Earth. As sunlight penetrates the atmosphere, it warms the planet. In turn, the Earth emits thermal radiation, which is subsequently absorbed and re-radiated by GHGs, thus retaining heat. This cycle is not inherently problematic; it is the amplification of this process that ignites our global concerns.
In recent decades, human endeavors—exemplified by industrialization, deforestation, and the insatiable quest for fossil fuels—have exacerbated the concentration of GHGs in the atmosphere. The decomposition of organic matter, agricultural practices, and waste management also contribute to this phenomenon. Consequently, we witness a marked increase in global temperatures, a reality encapsulated in the term “anthropogenic climate change.” This escalation is not merely an abstract concept; it translates to tangible consequences. Weather patterns shift dramatically, unpredictable storms rage, sea levels rise inexorably, and ecosystems teeter on the brink of collapse.
Yet, within this challenging narrative lies an opportunity—a transformative possibility for society to reshape its relationship with the environment. The awareness of the greenhouse effect catalyzes our curiosity about potential solutions and strategies. By understanding the culprits of GHG emissions, society can embark on a journey towards sustainable practices. The adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, can diminish reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate atmospheric pollution. This paradigm shift harbors the promise of not merely curbing emissions but also fostering economic growth through innovation and job creation in emerging green technologies.
Moreover, the importance of conservation cannot be overstated. Forests, often referred to as the lungs of our planet, play a crucial role in sequestering carbon. The act of reforestation—reviving degraded landscapes—can significantly bolster our ability to counterbalance carbon emissions and restore ecological integrity. Beyond trees, the preservation of wetlands and other ecosystems serve as natural buffers, critical in regulating climate and offering habitat to countless species facing extinction.
In our pursuit for solutions, international collaboration emerges as a cornerstone of effective climate action. Global initiatives, such as the Paris Agreement, illustrate how nations can unite in addressing climate change collectively. By setting ambitious targets to reduce emissions and enhance climate resilience, countries can foster a culture of accountability. Such cooperative efforts emphasize the need for holistic policies that transcend borders, advocating for a world where prosperity coexists harmoniously with ecological integrity.
The interconnectedness of the greenhouse effect with everyday life ignites a call for individual responsibility. As citizens, our choices resonate through the intricate networks of the environment. Opting for sustainable transportation—such as cycling or utilizing public transit—can diminish our carbon footprints considerably. Mindfully selecting products and lifestyles that emphasize sustainability reflects a commitment to preserving the planet for future generations. These seemingly inconsequential actions coalesce to create a powerful collective impact, sparking a widespread cultural awakening towards eco-consciousness.
Education lies at the heart of this awakening. Knowledge empowers individuals to understand the implications of the greenhouse effect, fostering a sense of agency—an understanding that change is possible. Schools, communities, and governments must champion initiatives that disseminate information about climate science, conservation practices, and the benefits of sustainable living. The cultivation of environmentally literate citizens will ultimately ensure a future that prioritizes the health of both the planet and its inhabitants.
In closing, while the greenhouse effect is a scientific principle that underpins our climate system, its ramifications extend far beyond mere temperature fluctuations. It stands as a reflection of our choices—the cumulative impact of individual actions and collective policies shaping the world we inhabit. Through understanding, we nurture awareness, and with awareness, we inspire action. The call is clear: to confront the challenges presented by climate change, we must embrace a paradigm shift, viewing the greenhouse effect not simply as a threat, but as an opportunity—an invitation to envision and forge a sustainable future.








Leave a Comment