The Greenhouse Effect is a phenomenon that evokes a sense of intrigue and contemplation among environmentalists and casual observers alike. At first glance, one might perceive it merely as a mechanism responsible for global warming. However, its role is multi-faceted and essential for sustaining life on Earth. To explore the vital purpose of the Greenhouse Effect, we must delve into the intricacies of atmospheric dynamics and the delicate balance that governs our planet’s climate.
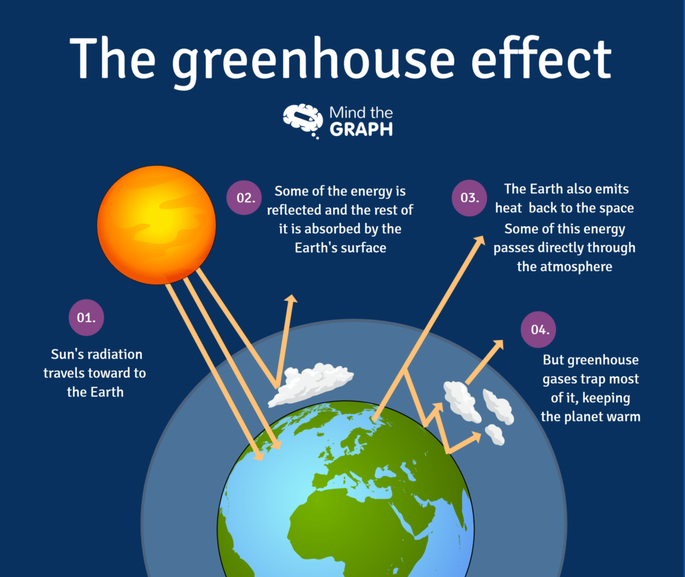
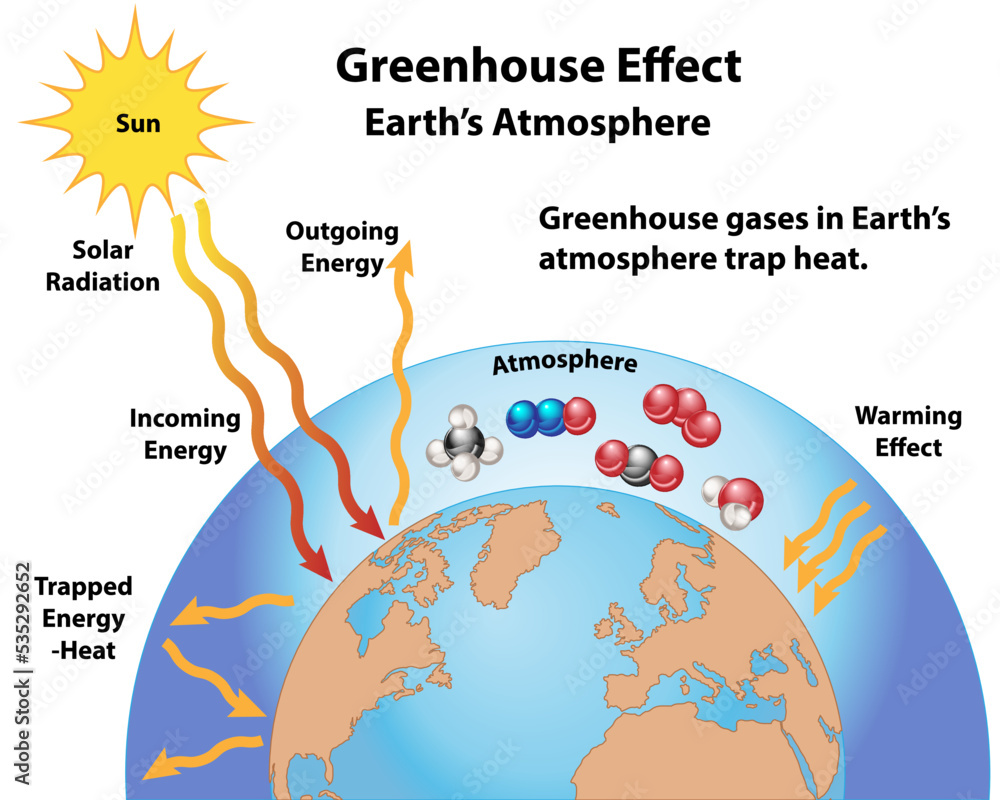
To grasp the significance of the Greenhouse Effect, one must first understand its fundamental workings. The Earth receives a substantial portion of energy from the sun, a radiant fusion reactor that fuels our planet’s ecosystems. This energy primarily arrives in the form of visible sunlight. As this energy strikes the Earth’s surface, it transforms into heat, which is then radiated back into the atmosphere in longer wavelengths. Herein lies the crux of the Greenhouse Effect: certain gases in the atmosphere, known as greenhouse gases, absorb and re-radiate this heat, creating a warming effect that is crucial for maintaining a stable climate.
Among the notable greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). These gases are not merely pollutants; they serve as the atmospheric blanket that preserves the warmth necessary for life. Without this natural insulation, the average surface temperature of the Earth would plummet to an inhospitable -18 degrees Celsius (0 degrees Fahrenheit) from the current mild average of about 15 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit). This stark contrast illuminates an essential truth: the Greenhouse Effect is not a villain in the climate narrative; rather, it is a fundamental ingredient that has nurtured and preserved the biosphere for eons.
By creating a stable thermal environment, the Greenhouse Effect facilitates a diverse array of ecological processes, some of which may not be immediately apparent. Consider the intricate tapestry of life, from the smallest microorganisms to majestic trees and expansive oceans. The warmth retained by greenhouse gases promotes photosynthesis, the cornerstone of food chains across our planet. Plants flourish under the sun’s embrace and, in turn, produce oxygen, which is indispensable for respiration in countless organisms. The process fosters the growth of forests, grasslands, and crop fields, cultivating biodiversity and contributing to the myriad ecosystems that define our world.
Another critical aspect of the Greenhouse Effect is its role in the hydrological cycle. Water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas, plays a dual role: it is both a contributor to the greenhouse effect and a vital component of weather patterns. By trapping heat, it enables the transformation of water into vapor, which ascends, cools, and eventually condenses into precipitation. This feedback loop not only replenishes freshwater resources but also helps regulate temperatures, underpinning agriculture and maintaining ecosystems. A delicate balance exists here; too much inflation of these gases can threaten this equilibrium, leading to adverse climatic events, but their presence is undeniably crucial.
Moreover, the Greenhouse Effect has imparted a sense of resilience to the climatic systems of our planet. While fluctuations in temperature are normal, the stabilizing influence of greenhouse gases has allowed our ecosystems to adapt to various climatic conditions over geological epochs. Fossil records reveal that life has thrived through epochs of warmth and cold, illustrating the capacity for adaptation and evolution spurred by this natural greenhouse. It is a narrative of survival and transformation, where life’s tenacity flourishes under the guardianship of greenhouse gases.
However, the current trajectory of anthropogenic emissions has engendered an existential threat to this natural balance. The unchecked proliferation of greenhouse gases, primarily stemming from human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes, has rendered the atmosphere increasingly saturated. This exacerbation of the Greenhouse Effect has forced the planet into an uncertain future, marked by extremes of temperature and unpredictable weather patterns. As guardians of this fragile environment, it is imperative that we understand the juxtaposition between the natural benefits of greenhouse gases and the perils of their excess.
The interaction between societal developments and natural phenomena points toward a symbiotic relationship that demands respect and stewardship. Initiatives aimed at enhancing energy efficiency, investing in renewable energy sources, and restoring natural ecosystems are pivotal steps toward mitigating the negative consequences of an inflated Greenhouse Effect. Understanding the delicate interplay between human activity and the atmospheric balance is crucial in crafting policy frameworks that prioritize ecological integrity while ensuring energy needs are met.
In conclusion, the Greenhouse Effect is not merely a scientific term laden with connotations of doom and gloom. Rather, it is a fundamental process that sustains life, fostering an environment teeming with biodiversity and interconnectedness. As we grapple with the looming specters of climate change and its ramifications, we must remind ourselves of the essential role the Greenhouse Effect plays. Recognizing its purpose compels us to advocate for a harmonious existence between humanity and nature, ensuring a vibrant and sustainable future for generations to come. Balancing the benefits of the greenhouse while curtailing its excessive manifestations is our collective responsibility, one that requires a deep appreciation for the very climate that nurtures us.







Leave a Comment