As global temperatures continue to rise due to anthropogenic activities, the phenomenon of sea level rise emerges as a critical concern. This escalating challenge is both multifaceted and alarming, posing existential threats to coastal populations and ecosystems. In this exploration, we dissect the mechanisms behind sea level rise and its profound implications for humanity and the environment.
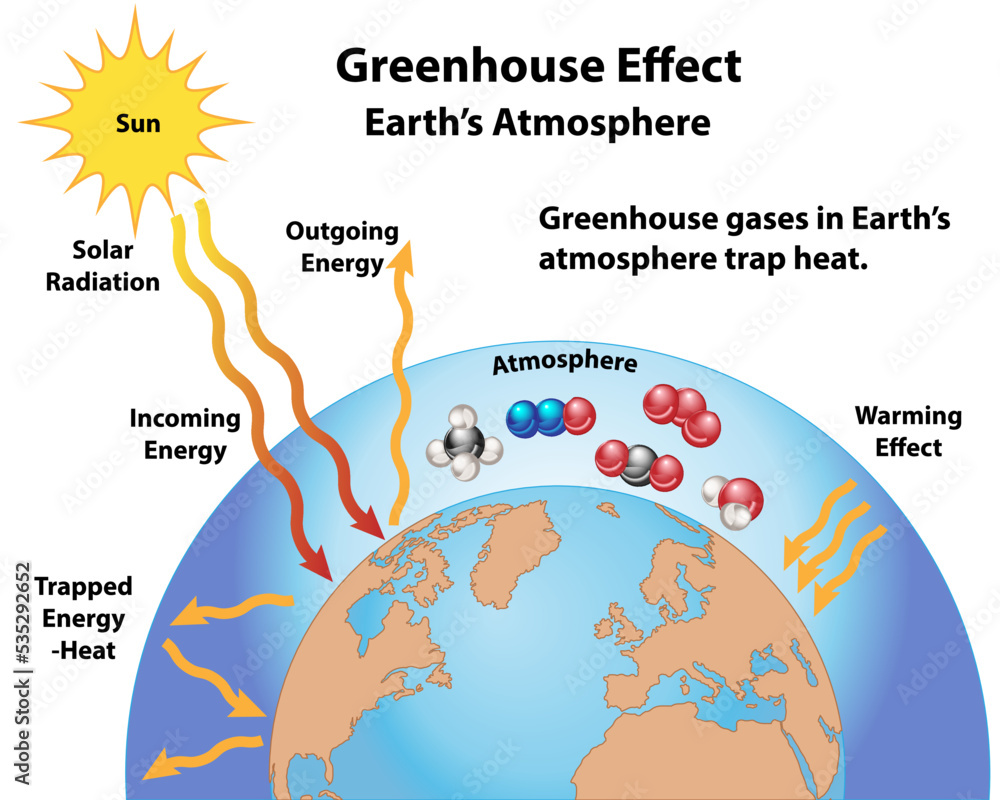
To begin with, understanding sea level rise necessitates an exploration of its underlying causes. The phenomenon primarily results from two interrelated processes: thermal expansion of seawater and the increase in water volume from melting ice. As the Earth’s atmosphere warms, ocean temperatures climb, causing seawater to expand. This thermal expansion contributes significantly to rising sea levels. Concurrently, the melting of glaciers and polar ice sheets—most notably from Greenland and Antarctica—introduces additional water into the oceans, exacerbating the problem. A confluence of these factors reveals a troubling trajectory; projections indicate that if emissions continue unabated, global sea levels could rise by several feet by the end of the century.
Geologically speaking, sea levels have fluctuated throughout history due to natural processes. However, the accelerated pace observed today is unprecedented and largely attributable to human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels which increases greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere. This anthropogenic impact not only amplifies global warming but also disrupts long-term climate patterns, yielding consequences far beyond traditional weather phenomena.
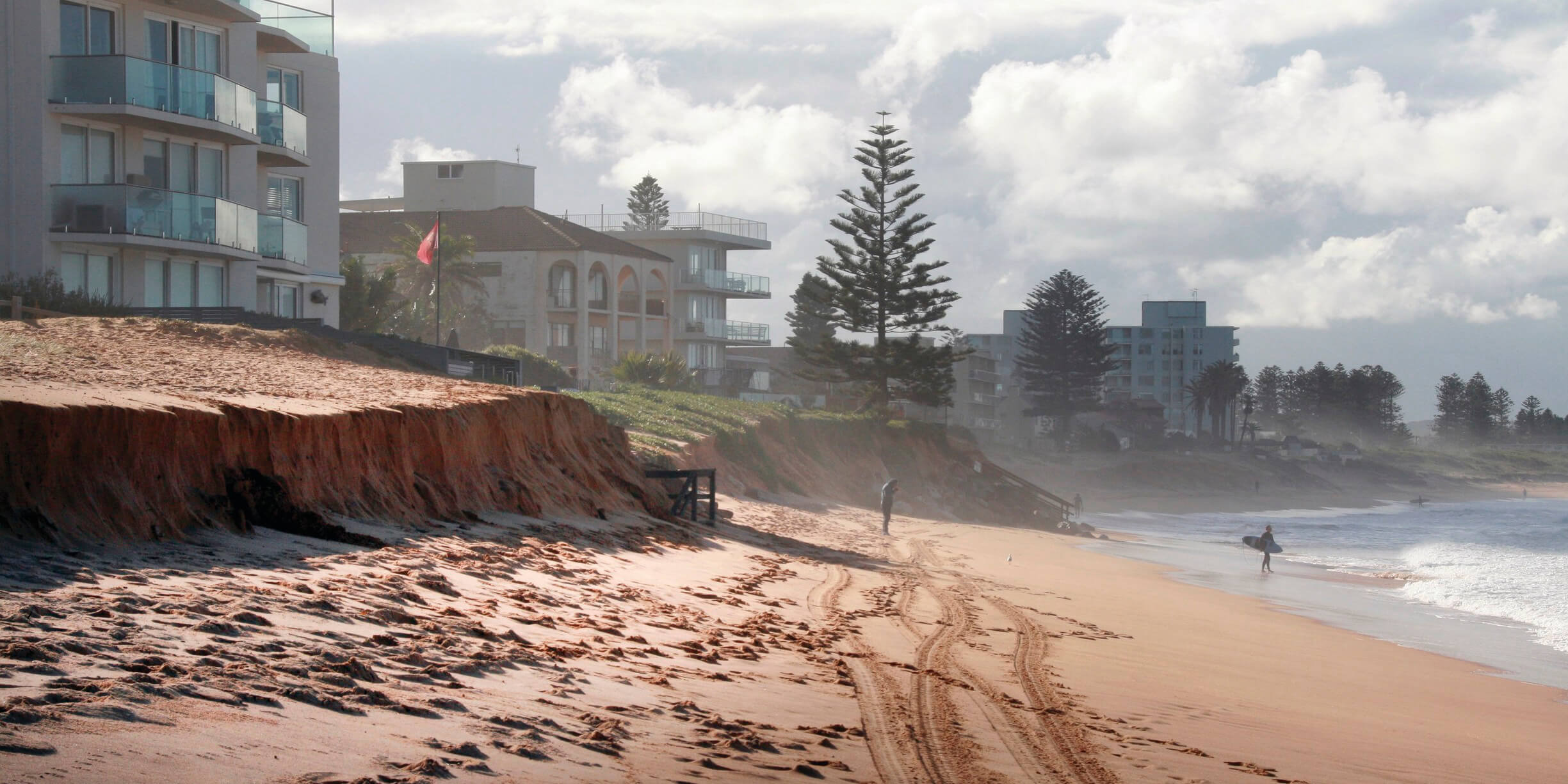
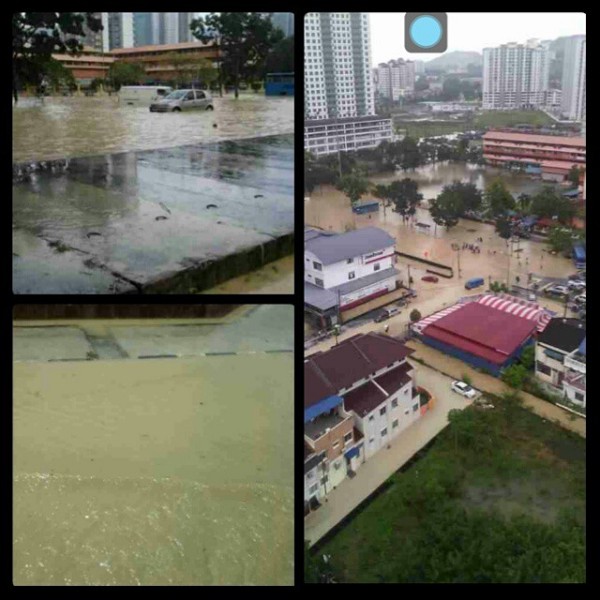
The implications of rising sea levels extend well beyond mere inches or feet. For coastal communities, the encroachment of ocean waters into inhabited areas poses a severe risk to infrastructure, freshwater supplies, and local economies. Urban centers situated along coastlines may find themselves grappling with increased flooding, particularly during storm surges exacerbated by climate change. Moreover, saltwater intrusion into aquifers threatens the availability of potable water in many regions. The specter of displacement looms large, with estimates suggesting that hundreds of millions may be forced to relocate in the coming decades due to the inundation of their homes.
Furthermore, the environmental ramifications are equally distressing. Coastal ecosystems, including wetlands and coral reefs, serve as vital buffers against storms and provide crucial habitat for countless species. The encroachment of saltwater can disrupt these delicate ecosystems, leading to biodiversity loss and degradation of natural habitats. As these ecosystems succumb to rising waters, the services they provide—such as carbon sequestration and shoreline protection—are irreparably compromised.
In response to these looming threats, nations around the globe are grappling with adaptation and mitigation strategies. These efforts range from constructing sea walls and levees to restoring natural barriers like mangroves and wetlands. Although these measures can offer temporary relief and protection, they must be viewed as part of a broader strategy that encompasses sustainable development and global cooperation on climate action.
International agreements such as the Paris Accord signify a pivotal step towards collective action against climate change. By committing to limit global warming to well below two degrees Celsius, nations aim to curtail further emissions and stabilize the climate. However, the effectiveness of these agreements hinges on accountability, implementation, and the willingness of nations to prioritize long-term planetary health over short-term interests.
Ultimately, the urgency surrounding sea level rise serves as a stark reminder of our interconnectedness. It underscores the need for individuals to engage in climate action and advocacy. Each person can contribute, whether through reducing their carbon footprint or supporting policies aimed at sustainable environmental practices. Public awareness is pivotal; educating communities about the realities of climate change and its local manifestations can galvanize grassroots movements for change.
In conclusion, the phenomenon of sea level rise elucidates the comprehensive impacts of climate change on our oceans and coastlines. This challenge compels both individuals and nations to act with foresight, prioritizing the preservation of our planet for future generations. A concerted effort encompassing education, adaptation, and steadfast commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions is essential. As we navigate the uncertain waters ahead, understanding and addressing the intricacies of sea level rise will be paramount in shaping a resilient and sustainable future.








Leave a Comment