In recent years, the conversation surrounding renewable energy has ascended to the forefront of global discourse. Wind energy, in particular, has garnered increasing attention for its capacity to contribute to a more sustainable future. As nations grapple with the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate climate change, one question stands out prominently: how much electricity does wind energy generate globally?
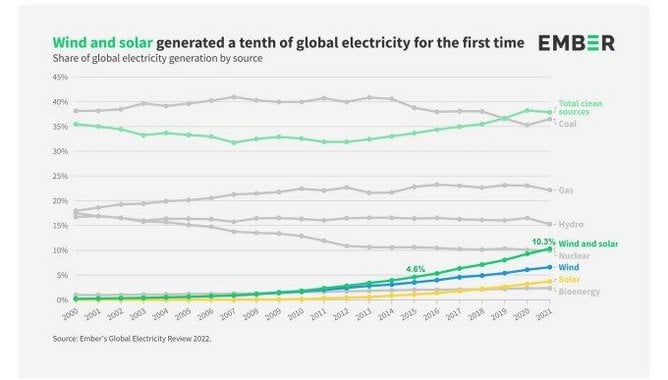
The answer to this inquiry is not merely about numbers or statistics; it embodies a narrative of transformation, innovation, and commitment to reversing environmental degradation. Currently, wind energy is capable of producing roughly 10% of global electricity. This statistic, while seemingly straightforward, represents a monumental shift in energy paradigms over the past few decades. It is essential to explore the circumstances leading to this growth, as well as the implications of its persistence and enhancement.
The inception of wind energy as a significant player in the electricity generation landscape can be traced back several decades. Initially dismissed as an unreliable alternative, advancements in technology have altered this perception radically. Improved turbine designs and enhanced efficiency have propelled wind energy to a position where it is no longer viewed as an auxiliary element, but rather a principal contender in the quest for clean power. This technological evolution has allowed wind farms to proliferate, occupying vast stretches of land and harnessing the natural force of the wind.
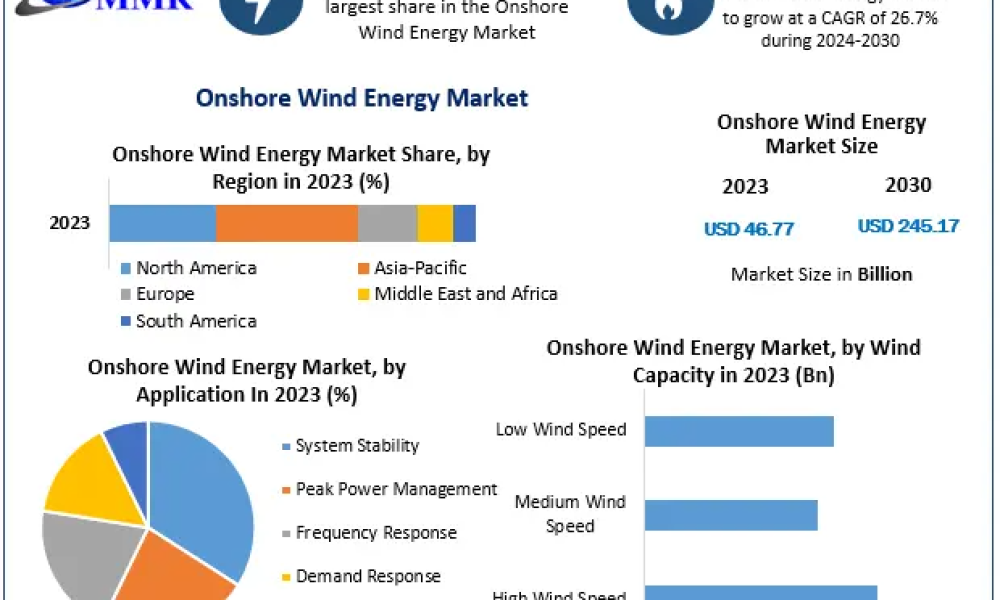
Geographically, the distribution of wind energy generation is anything but uniform. Countries such as China, the United States, and Germany are at the forefront of wind power utilization, each wielding significant contributions to the global electricity supply. China, in particular, has emerged as a veritable behemoth in this domain, investing heavily in wind infrastructure and innovation, resulting in the largest installed wind capacity in the world. This national prioritization of renewable energy not only fuels their grid but also sets a precedent for emerging economies seeking sustainable growth.
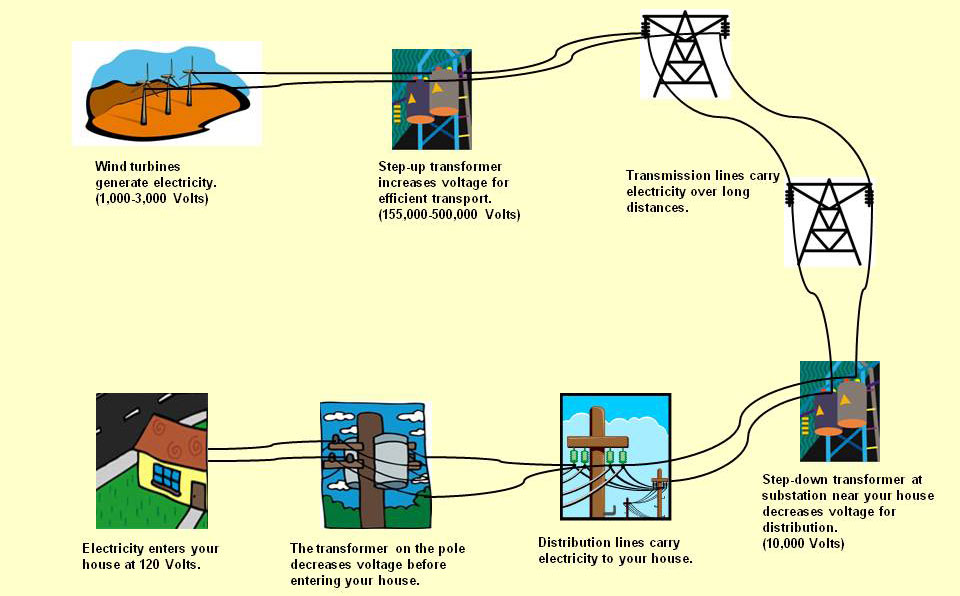
The mechanisms through which wind energy is generated can be quite captivating. Wind turbines, towering in stature, convert kinetic energy into mechanical energy, which is subsequently transformed into electrical energy. This process not only reflects the ingenuity of human engineering but also emphasizes the symbiotic relationship we have with our environment. The very act of harnessing wind—the unseen force—illustrates a profound respect for nature’s capabilities, one that recognizes the necessity of coexistence and sustainability.
However, the transition toward a wind-dependent energy ecosystem is fraught with challenges. One of the predominant concerns revolves around the intermittency of wind. Unlike coal or natural gas, wind energy generation is not constant; it ebbs and flows in tandem with natural wind patterns. This variability poses a conundrum for energy grid management, requiring advancements in energy storage technologies and grid integration to ensure reliability. As innovative solutions are unveiled—like battery storage and enhanced grid flexibility—the apprehensions surrounding intermittency gradually diminish, reinforcing confidence in wind as a reliable energy source.
Moreover, the environmental implications of wind energy extend beyond the immediate scope of electricity generation. Compared to fossil fuels, wind energy exhibits a markedly lower carbon footprint, thus contributing substantially to environmental preservation. Wind energy’s contribution to global electricity generation plays a pivotal role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, showcasing an unequivocal pathway toward combatting climate change. When considering the broader picture, the expansion of wind power signifies an evolution in energy ethics—one where environmental responsibility is increasingly intertwined with economic necessity.
Nevertheless, the pursuit of wind energy is not without its critiques. It is crucial to engage with the multifaceted implications that accompany wind farm establishment. Some argue that large-scale wind projects disrupt local ecosystems and habitats. The presence of turbines may also provoke concerns regarding noise pollution and aesthetic considerations for nearby communities. Engaging with local populations and understanding these issues is essential in harmonizing renewable energy expansion with community needs and environmental stewardship.
The global embrace of wind energy encapsulates a broader movement toward sustainable practices and innovation. Governments, private entities, and individuals have begun to recognize that our resources are finite, and the time for ample transformation is now. This recognition has catalyzed policy reforms worldwide, fostering an environment that encourages investment in renewable technologies. As electric vehicles gain traction and energy efficiency becomes a central tenet in modern infrastructure, the interdependence between these trends and wind energy becomes increasingly evident.
Looking to the future, the potential for expansion in wind energy generation is tremendous. With continued advancements in technology, a growing workforce skilled in renewable energy, and increasing global cooperation on climate initiatives, the share of wind energy in the global electricity mix is poised to rise. Nations must galvanize efforts to implement supportive policies that advocate for clean energy and invest in innovation, paving the path toward a greener tomorrow.
In summary, the statistic that wind energy generates approximately 10% of global electricity serves as a beacon of hope amidst a backdrop of environmental uncertainty. It signifies the indomitable spirit of human ingenuity and collaboration. While challenges remain, the trajectory of wind energy reflects not just an energy source, but a commitment to embracing a sustainable future. As we continue to navigate the complexities of energy demands and environmental responsibilities, wind energy stands as a powerful testament to what can be achieved when innovation meets necessity, illuminating the path ahead for generations to come.






Leave a Comment