Wind energy, one of the most promising renewable sources of power, has emerged as a formidable contender in the global shift towards sustainable energy. But how is this invisible force—a product of the Earth’s atmospheric dynamics—transformed into a tangible resource that powers homes, industries, and cities worldwide? This exploration into the harnessing and utilization of wind energy reveals both its marvels and challenges.
The genesis of harnessing wind energy can be traced back to ancient civilizations. Wind was first utilized for sailing ships, granting humanity the ability to traverse oceans and connect disparate lands. However, it was in the late 19th century that the true potential of wind as an energy source began to be recognized, coinciding with the development of wind turbines designed for electricity generation. Today, this technology has evolved exponentially, yet many may ponder: Are we truly maximizing the potential that wind energy offers? Or have we only scratched the surface of this ecological treasure?
To comprehend how wind energy is harnessed, one must first grasp the fundamental principle of the wind itself. Wind is generated due to uneven heating of the Earth’s surface by the sun. Areas that absorb heat differently create variations in air pressure, causing air to move from high-pressure zones to low-pressure zones. This movement of air is what we perceive as wind. But how does this kinetic energy transform into electrical power?
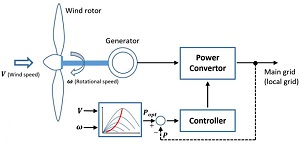
The answer lies in the modern wind turbine—a sophisticated machine that captures wind energy and converts it into electricity. A wind turbine consists of several key components: blades, a rotor, a nacelle, and a tower. The blades, typically made of lightweight composite materials, are designed aerodynamically to capture the maximum amount of wind. As the wind blows, it causes the blades to rotate, turning the rotor connected to a generator housed within the nacelle. This mechanical energy is then converted into electrical energy and sent to power grids for distribution.
Globally, wind energy has transcended its initial applications, evolving into vast wind farms. These installations, often found both onshore and offshore, harness the power of winds at different altitudes and locations. Onshore wind farms are increasingly common in regions with robust wind resources, such as the Great Plains in the United States or parts of Europe, where uninterrupted gusts can be captured to generate substantial electricity. Conversely, offshore wind farms, while more costly to install, exploit stronger and more consistent wind currents available over oceans, leading to a higher efficiency in energy production. The challenge here is maintaining a balance between ecological preservation and the burgeoning demand for energy—can we ensure that these wind installations do not disrupt marine and avian life?
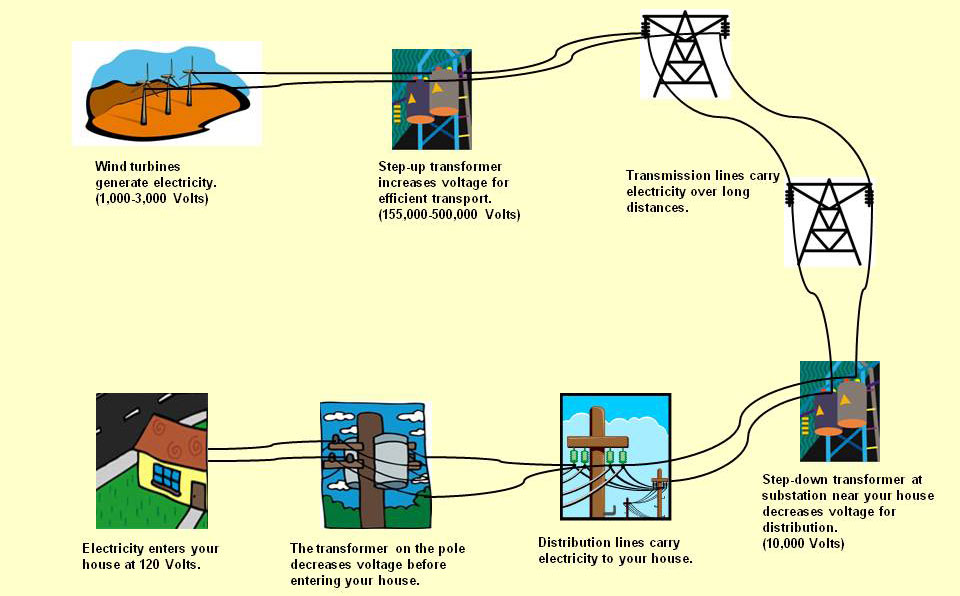
Once harvested, the wind energy undergoes a series of transformations before it supplies the electricity demanded by households and industries. This involves complicated infrastructure that includes transmission lines and substations. Electricity generated in remote wind farms is often transmitted over long distances to reach urban centers where demand is highest. However, this presents substantial logistical challenges. Transmission losses, capacity constraints, and the need for energy storage solutions are but a few hurdles that must be navigated in successfully integrating wind energy into the existing energy landscape. The question arises: Is our energy infrastructure robust enough to adapt to the rapid proliferation of renewable energy sources like wind?
Despite these challenges, the benefits of wind energy are far-reaching. It is one of the cleanest sources of energy, emitting no greenhouse gases during operation. Wind energy has a minimal carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels and is pivotal in combating climate change. Furthermore, it offers energy security by diversifying the energy mix—a crucial aspect in today’s geopolitically charged environment. Countries with abundant wind resources can reduce their dependence on imported fossil fuels, enhancing both economic stability and environmental integrity.
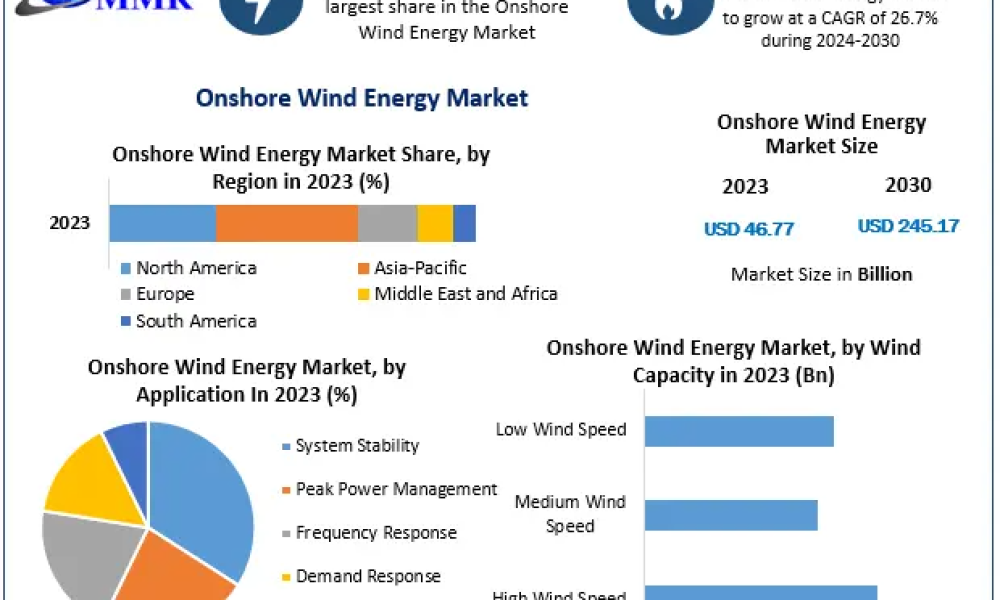
Wind energy is not merely a flash in the pan; its global adoption is gaining momentum. According to reports, countries such as China, the United States, and Germany are leading the charge in wind energy production. In China, staggering investments in renewable technology have catapulted it to the forefront of wind energy production, while the United States has leveraged its vast natural resources to become one of the largest producers globally. However, the proliferation of wind energy is not without its controversies; debates on aesthetics, noise pollution, and impact on landscapes highlight the complexities associated with its growth. As communities evaluate how to integrate wind farms into their locales, ongoing dialogues are essential. How do we balance progress with the intrinsic value of our natural landscapes?
Looking ahead, the future of wind energy appears promising yet fraught with challenges. With advancements in turbine technology, energy storage solutions, and smart grid infrastructure, the horizon seems brighter than ever. Enhancements in turbine efficiency, such as larger blades and improved materials, could increase energy output and decrease costs, making wind energy more accessible. Moreover, ongoing innovations in energy storage, including batteries and pumped hydro storage, promise to mitigate the intermittency issues that wind energy often faces, thereby ensuring a reliable power supply regardless of weather conditions.
In conclusion, the journey of harnessing wind energy is one that encompasses ingenuity, perseverance, and a steadfast commitment to sustainability. As the world grapples with the imperatives of climate change and the urgent need for energy transformation, the question remains: Are we prepared to embrace this inexhaustible source of energy fully? Will society rise to meet the challenge, ensuring that this powerful resource is utilized wisely, ethically, and effectively for future generations? The winds of change are blowing, and it is incumbent upon us to harness their potential responsibly and innovatively.







Leave a Comment