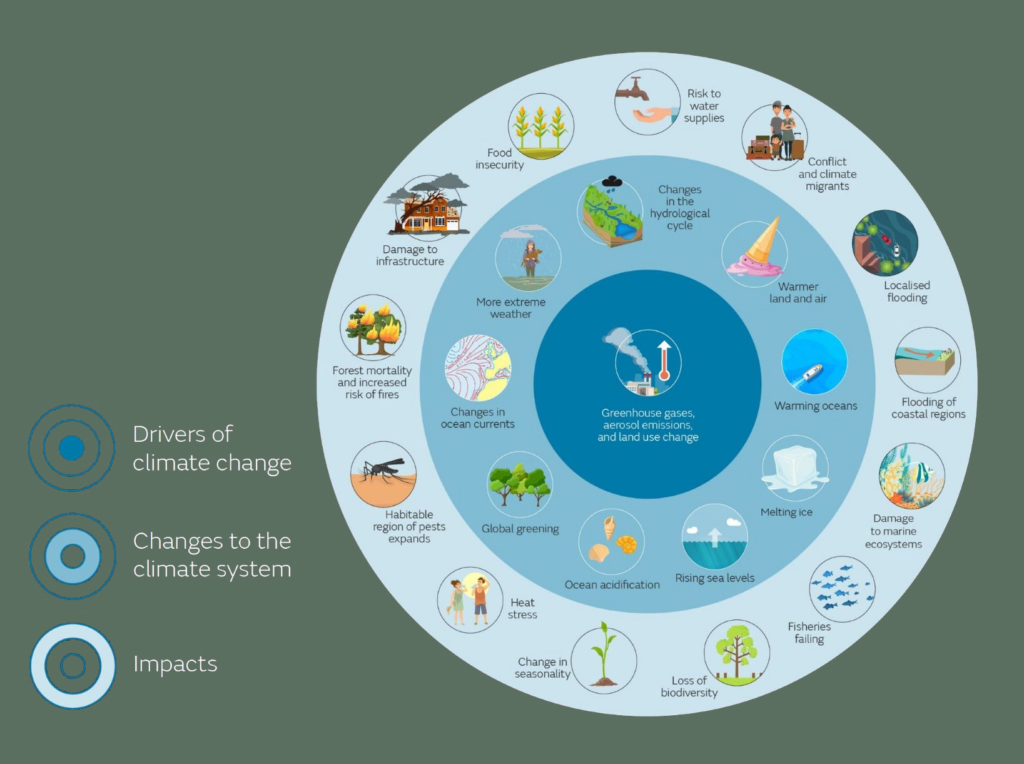
The question of whether climate change is affecting local weather patterns is becoming increasingly pertinent as unusual climatic phenomena unfold across the globe. As temperatures rise, patterns of precipitation fluctuate, and extreme weather events become more frequent, the impact of climate change on our everyday weather has reached a point where it can no longer be ignored. This article delves into the various ways climate change manifests in local weather, backed by compelling evidence and observations.
1. Changes in Temperature Extremes
One of the most salient indicators of climate change is the increase in the frequency and intensity of temperature extremes. Regions that once enjoyed mild seasons are now experiencing sweltering summers and bitterly cold winters. This shift is not merely a statistical anomaly; it is a symptom of global warming that has disrupted long-standing weather norms.
For instance, urban areas known for their moderate climates are facing unprecedented heatwaves, leading to a surge in heat-related illnesses and strain on local energy resources. In contrast, regions traditionally characterized by frigid winters now contend with sporadic warm spells that disrupt ecological cycles. The ramifications extend beyond mere discomfort; they threaten the agricultural calendar and local flora and fauna, which struggle to adapt to these abrupt changes.
2. Alterations in Precipitation Patterns
Climate change is not solely a harbinger of warmth; it profoundly influences precipitation patterns. The frequency, intensity, and distribution of rainfall are shifting, resulting in increasingly anomalous weather events. Some regions are inundated with excess rainfall, leading to catastrophic flooding, while others face prolonged drought, devastating local agriculture and water supplies.
Statistical analyses reveal that many locales previously accustomed to predictable rainfall are now confronting erratic precipitation. Agriculture—an industry heavily reliant on weather constancy—finds itself in a precarious position. Crop failures occur as farmers struggle to cope with either excess moisture or insufficient rainfall, further exacerbating food insecurity. The broader economic ramifications of these changes cannot be overstated, as they reverberate through local communities that depend on farming and related industries.
3. The Escalation of Extreme Weather Events
The frequency of extreme weather events has escalated alarmingly, correlating strongly with rising global temperatures. Hurricanes, tornadoes, and severe thunderstorms are no longer relegated to their historical norms; they are becoming increasingly unpredictable in both intensity and occurrence. Regions that once faced occasional hurricanes now brace for multiple storms each season, with property damage and loss of life following in their wake.
Moreover, the connection between climate change and extreme weather is underscored by scientific inquiry, which demonstrates that warmer air holds more moisture. This fact results in storms that deliver heavier rains and stronger winds, leading to more devastating impacts on communities. The cost of recovery from such disasters, both financially and socially, is staggering, illuminating the urgent need for climate action.
4. The Influence on Ecosystems and Wildlife
The ramifications of climate change on local weather conditions flow not just into human experience but also reverberate through ecosystems and wildlife. Species that have thrived in particular climates face existential challenges as their habitats transform. Shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns can lead to mismatched timings in migration and breeding, with some species unable to adapt quickly enough to survive.
Local ecosystems are responding to changing conditions, potentially leading to shifts in biodiversity. In many instances, invasive species take advantage of warmer temperatures, outcompeting native flora and fauna, and further stressing ecosystems struggling to adapt. With each species that struggles to survive, the intricate web of life crumbles a little more, undermining the health of our planet and the services it provides.
5. Economic and Social Implications
The socio-economic consequences of climate-induced weather changes are profound. Communities across the globe are grappling with the repercussions, from increased health care costs due to heat-related illnesses to economic losses in agriculture and tourism. Vulnerable populations, particularly in developing nations, bear the brunt of these changes, often lacking the infrastructure and resources necessary to adapt.
As weather patterns shift, local governments and communities must invest in resilience planning. This includes developing infrastructure to withstand flooding, implementing water conservation measures, and updating emergency response protocols to deal with the growing frequency of extreme weather events. The interconnectedness of climate and societal stability cannot be overstated; as weather becomes more unpredictable, so too does the fabric of our communities.
6. The Path Forward: Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Given the pervasive influence of climate change on local weather patterns, mitigation and adaptation strategies are imperative. Communities must collectively recognize the urgency of the issue and take action toward reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and advocating for sustainable agricultural practices are vital steps in combatting climate change.
Simultaneously, adaptation strategies must be developed to manage the impacts already in motion. This includes investing in green infrastructure, promoting water conservation, and fostering community resilience through education and awareness programs. The future of our local weather—and, by extension, our communities—hinges upon proactive measures that address both the causes and consequences of climate change.
In conclusion, climate change is indelibly affecting local weather patterns, with evidence manifesting in temperature extremes, altered precipitation, increased severity of extreme weather events, and substantial impacts on ecosystems and communities. By acknowledging these changes and taking concerted action, we can work towards creating a more sustainable future, where our local weather patterns stabilize and the health of our planet is preserved for generations to come.








Leave a Comment