When you see towering wind turbines gracefully spinning against the vast landscape, have you ever contemplated the intricate process that transforms blustering winds into usable electricity? It’s a remarkable demonstration of engineering ingenuity, harnessing nature’s most abundant resource. In this exhaustive exploration, we will delve into the process of how a wind power station generates electricity step by step, shedding light on the numerous elements that contribute to this sustainable form of energy.
At the core of wind energy generation is the wind turbine, a majestic structure designed to capture kinetic energy from the wind. While one might be captivated by their imposing height and elegance, the real magic lies beneath the surface. The foundation of a wind power station is a veritable labyrinth of technology and design, working in harmony to convert wind into electrical energy. But what exactly happens when the wind greets a turbine? Let’s embark on this enlightening journey, one step at a time.
First and foremost, the process begins with the wind itself. Wind is the result of atmospheric pressure differences, primarily driven by the sun’s uneven heating of the Earth’s surface. As warm air rises and cool air moves in to take its place, gusts of wind are created. Interestingly, wind speeds must reach a minimum threshold—often around 3 to 4 meters per second—before they become conducive for generating electricity. If the wind is too calm, the turbines remain idle; however, if it exceeds a certain speed, typically around 25 meters per second, the turbines will shut down to prevent damage. Isn’t it fascinating how nature dictates the operations of these machines?
Once the wind reaches the necessary velocity, it flows over the blades of the wind turbine. Wind turbines are designed with specifically engineered blades, often resembling those of an aircraft wing. When the wind strikes the blades, it generates lift, causing the blades to rotate. The rotation speed can reach impressive levels, making the wind turbine appear as a flurry of motion against the skyline. This conversion of wind’s kinetic energy into rotational energy marks an essential juncture in the electricity generation process.
As the blades turn, they are connected to a shaft that leads down to the gearbox. This component is crucial; it increases the rotational speed from the relatively slow rotation of the blades (approximately 10 to 20 revolutions per minute) to a much higher rate that is required to generate electricity (around 1,500 revolutions per minute for most generators). The gearbox effectively transforms low-speed, high-torque rotation into high-speed rotation, set for the next phase of the process. However, the transformation is not without challenges. Gearboxes can be subject to mechanical wear and tear, raising questions about maintenance and longevity.
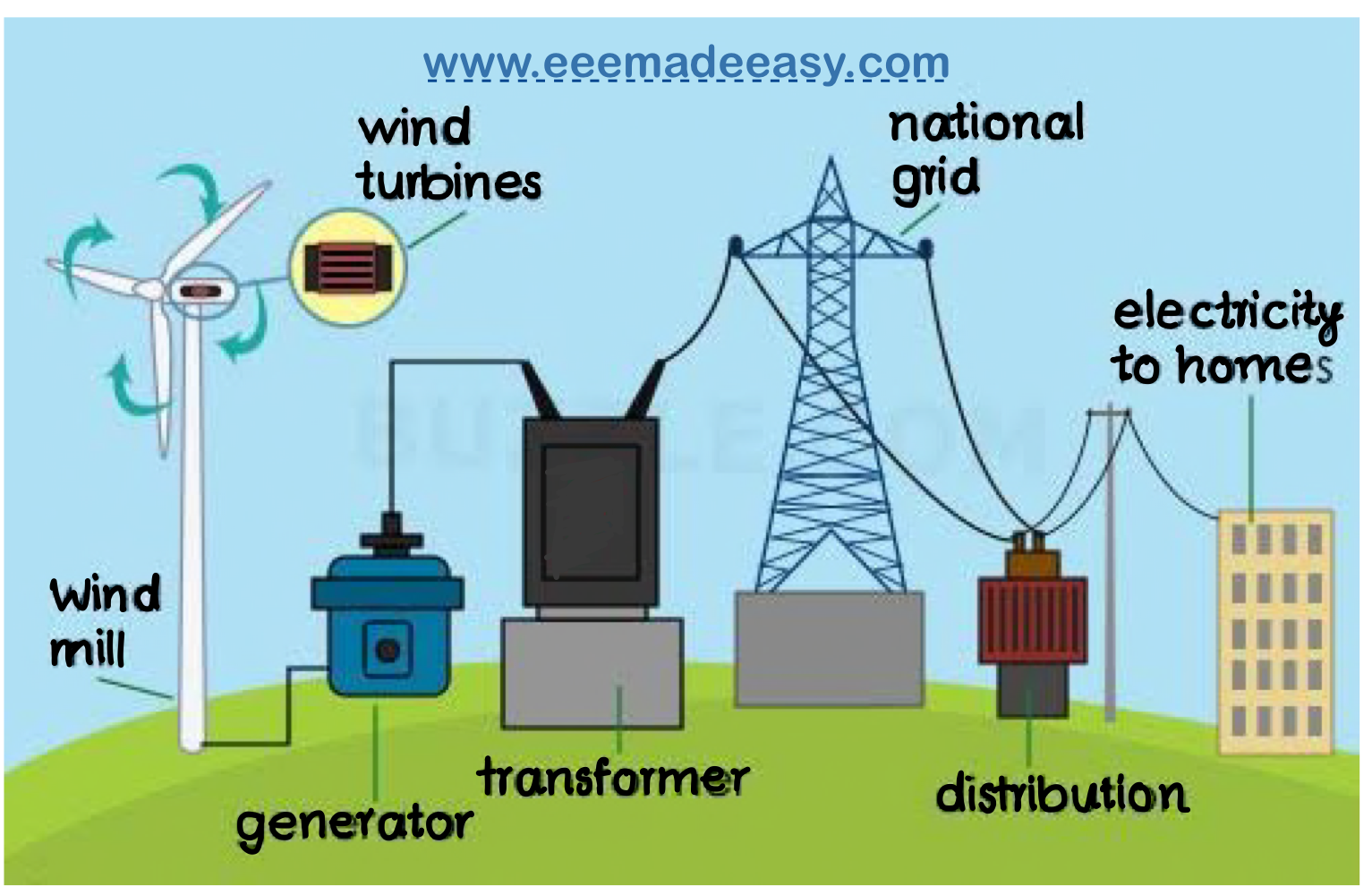
Once the kinetic energy is escalated through the gearbox, it reaches the generator. Here, electromagnetic induction takes center stage. The generator consists of magnets and coils of wire. As the fast-moving shaft spins the rotor (the rotating part), it induces a flow of electromagnetic energy in the stationary coils of wire. This meticulously orchestrated dance of components ultimately converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, effectively birthing volts of electricity ready for distribution.
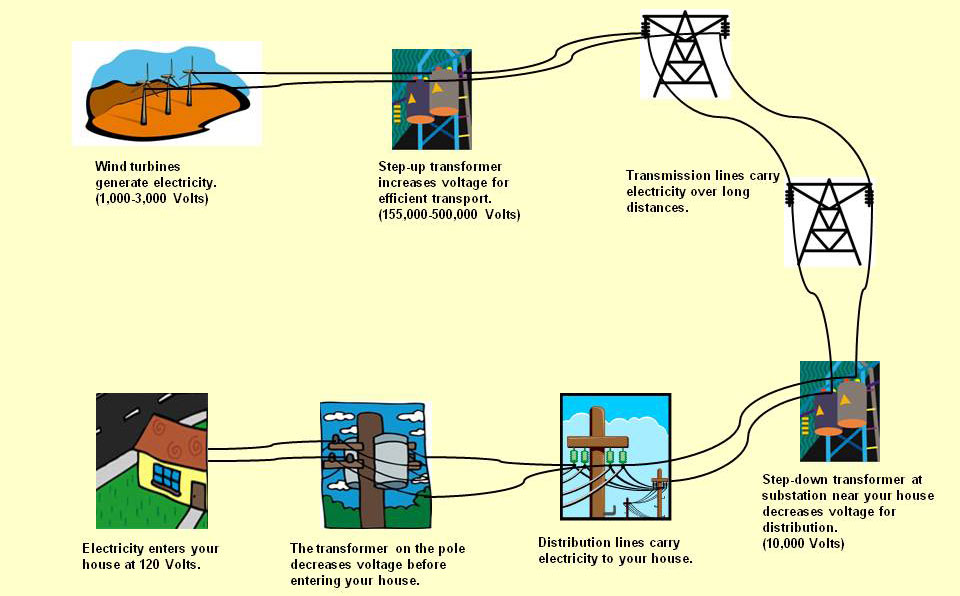
The generated electricity, however, finds itself in an immediate need; it is in alternating current (AC) form, which must be appropriately handled. In order to make this energy usable in homes and businesses, it undergoes a transformation. A power inverter is employed to convert the electricity from AC to direct current (DC) when necessary, and it stabilizes the voltage to ensure compatibility with the grid. Herein lies a crucial challenge: fluctuations in wind speed can lead to inconsistencies in power output, necessitating well-designed inverters that manage variations and ensure reliability. Without efficient voltage stabilization, the harmony between renewable energy sources and the grid can be easily disrupted.
As the electricity is prepared for distribution, it heads towards the transformer, a vital apparatus that increases the voltage for transmission purposes. High-voltage electricity is essential for minimizing energy loss over transmission lines, which can be significant when electricity travels long distances. The transformer thus ensures that energy can be dispatched effectively to homes, businesses, and industries. Have you ever paused to think about the journey this electricity embarks on as it travels from the windswept turbine to the light bulb illuminating your room?
After undergoing these critical transformations, the electricity enters the power grid, where it is distributed according to demand. This entire mechanism operates seamlessly, with numerous turbines often connected in a wind farm to create a robust power generation substation. Connecting multiple turbines enhances reliability and efficiency, further promoting the advantages of wind energy as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
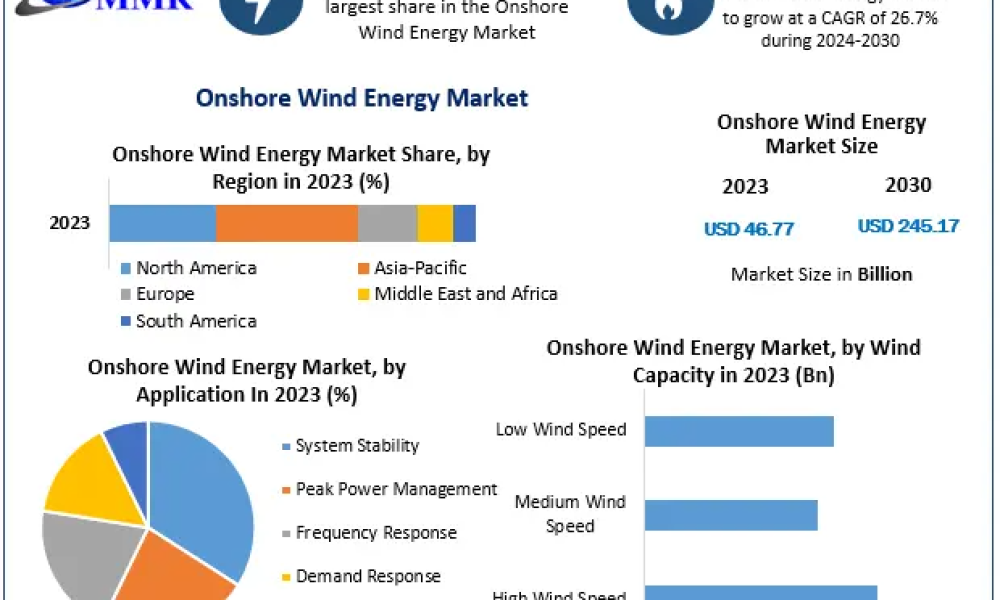
The advantages of harnessing wind power are immense. It is a clean and inexhaustible source of energy, significantly reducing our carbon footprint compared to conventional energy sources. Furthermore, the proliferation of wind farms stimulates local economies, provides job opportunities, and increases energy independence. In contrast, challenges do remain—regarding land use, the impact on wildlife, and the visual aesthetics of wind farms when placed near residential areas. Balancing these aspects is part of the ongoing discourse surrounding renewable energy development.
In conclusion, the powerful synergy of mechanical engineering and natural phenomena in a wind power station is a testament to human ingenuity. While advancements in technology continue to emerge, refining and optimizing each step remains paramount. The future of energy generation is intertwined with sustainable practices, and wind power serves as a beacon of hope in our collective quest for a cleaner, greener planet. So, next time you witness the turbines spinning against the backdrop of the sky, take a moment to appreciate the intricate ballet of technology and nature unfolding silently before your eyes.







Leave a Comment