In a world increasingly dominated by relentless energy demands and the omnipresent specter of climate change, wind energy emerges as a paragon of sustainability—a gentle giant harnessing the very breath of our planet. Picture a vast, rolling landscape adorned with towering turbines, their blades gracefully spinning against the backdrop of azure skies. Herein lies an ode to wind energy, a comprehensive beginner’s guide illuminating its mechanisms, advantages, challenges, and the profound impact it can wield on our collective future.
The Nature of Wind Energy
Wind energy is birthed from the sun’s uneven heating of the Earth’s surface, which orchestrates the movement of air; warm air ascends while cooler air rushes in to fill the void. This intricate dance results in wind—an invisible stream of kinetic energy that can be captured and transformed into a potent source of electricity through the innovative technology of wind turbines. Each turbine stands as a sentinel, converting the ethereal whispers of the wind into the tangible pulse of electric power.
How Wind Turbines Work
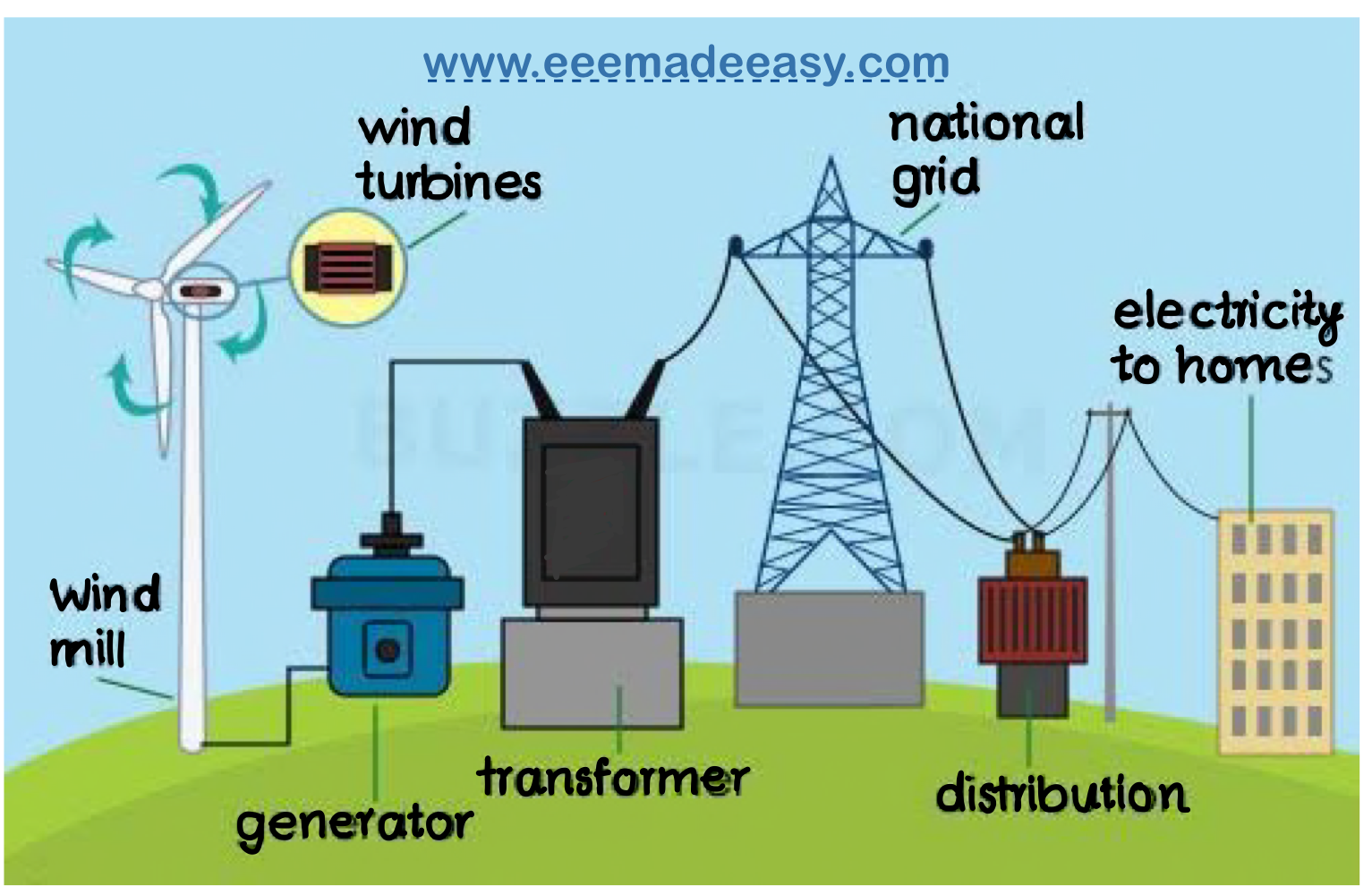
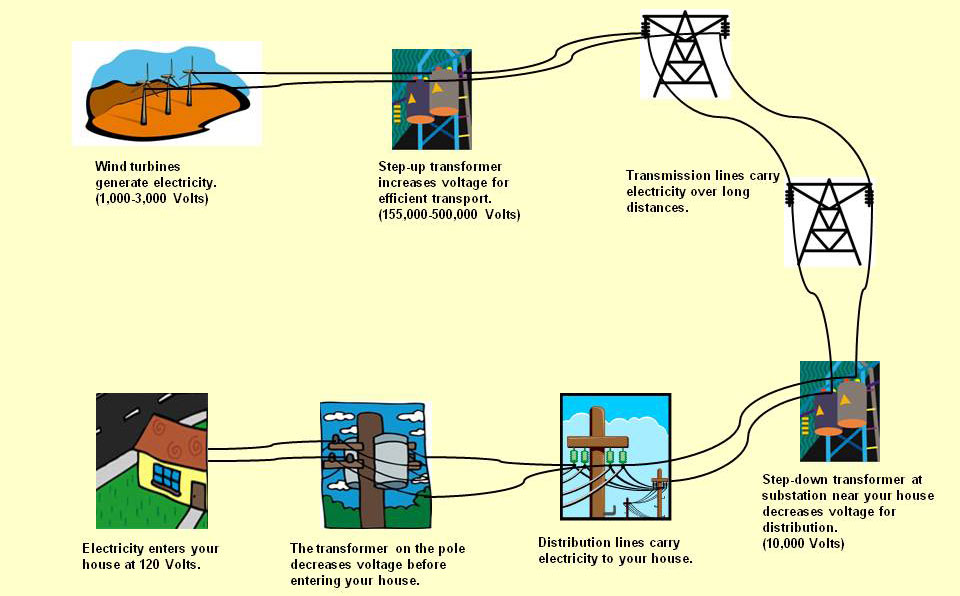
At the heart of this phenomenon lies the wind turbine, a remarkable amalgamation of engineering and ecological wisdom. Comprised of three primary components—the rotor, the gearbox, and the generator—these giants function by allowing wind to flow over the blades, causing them to rotate. This mechanical motion is subsequently transmitted to a gearbox, which amplifies the rotational speed before it reaches the generator. It is at this juncture that kinetic energy metamorphoses into electrical energy, thus lighting homes and powering industries.
The Types of Wind Energy Systems
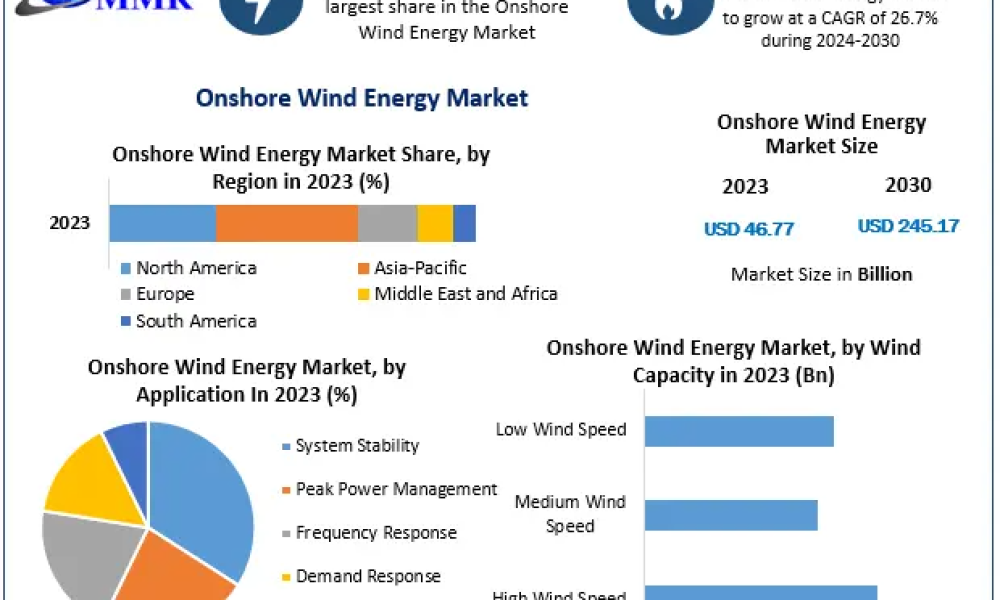
Wind energy systems can be broadly categorized into two distinct types: onshore and offshore. Onshore wind farms, situated on land, have become ubiquitous in regions endowed with consistent wind patterns. Conversely, offshore wind farms capitalize on the immense, uninterrupted gusts found over oceans and large bodies of water, often harnessing stronger and more reliable winds. These offshore installations are akin to modern-day galleons, sailing upon the sea’s surface, unfurling their sails to capture nature’s bounty.
The Advantages of Wind Energy
Numerous advantages envelop wind energy, marking it as a front-runner in the quest for greener alternatives. First and foremost, wind power is renewable—a constant companion in our lives as long as the sun casts its rays. Further underscoring its appeal is its minimal carbon footprint. Unlike fossil fuels, which release harmful greenhouse gases, wind energy represents a pristine choice, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier planet.
Additionally, sector growth in wind energy fosters economic stimulation. Communities that embrace wind farms witness job creation, from turbine manufacturing to maintenance and operational management. This burgeoning industry bolsters local economies and, in turn, engenders a sense of pride as communities invest in sustainable futures.
Moreover, unlike conventional energy sources, wind energy generates electricity devoid of water consumption, conserving this precious resource in a world where water scarcity looms large. This pivotal trait embodies a resilience that augurs well for biomes and local ecosystems.
The Challenges Ahead
Challenges ensue, however, in the pursuit of wind energy. For instance, the inconsistency of wind poses a significant dilemma. Not all geographical regions exhibit the same wind potential, leading to disparities in energy production. Additionally, the intermittent nature of wind necessitates robust storage solutions —if the wind doesn’t blow, the turbines remain still, creating potential gaps in energy supply.
Beyond technical hurdles, societal concerns manifest. The aesthetics of wind turbines provoke conversation, as some view these behemoths as unsightly additions to idyllic landscapes. Moreover, issues concerning avian fatalities arise, where bird collisions with turbine blades occur. Addressing these concerns requires innovative solutions such as strategic siting, bird monitoring systems, and turbine designs that minimize harm.
The Future of Wind Energy
As we gaze toward the horizon of energy innovation, the future of wind energy gleams with promise. Technological advancements increasingly enhance turbine efficiency, with larger, more sophisticated blades capturing more wind while operating quietly and seamlessly. Innovations in offshore capabilities herald a new era—floating turbines unlock access to previously unreachable wind corridors, expanding the vast potential of this renewable resource.
Furthermore, integration with other renewable sources, such as solar energy, heralds an era of hybrid systems, maximizing resource potential and reducing dependency on a singular form of energy. As global awareness burgeons, governments are steadfastly implementing policies that advocate for renewable energy investments, propelling wind energy into the forefront of the energy transition.
A Call to Action
In conclusion, wind energy stands not merely as an alternative source of power but as an embodiment of the harmonious interplay between humanity and nature. By fully embracing the wind’s potential, we can carve a sustainable path forward, nurturing the world we inhabit. Each turn of a turbine’s blades not only signifies the electrification of homes but also represents a stride toward a more sustainable and united future. We must champion the causes of renewable energy, forging a collective commitment that reverberates through time, like the steadfast breeze navigating the contours of our planet. The winds of change are upon us; let us not merely watch them pass but engage, innovate, and embrace the change they herald.






Leave a Comment